Angular 4 - 快速指南
Angular 4 - Overview
Angular有三个主要版本。 发布的第一个版本是Angular1,也称为AngularJS。 Angular1之后是Angular2,与Angular1相比,它有很多变化。
Angular的结构基于组件/服务体系结构。 AngularJS基于模型视图控制器。 2017年3月发布的Angular 4被证明是一项重大突破,是Angular团队在Angular2之后发布的最新版本。
Angular 4与Angular 2几乎相同。它与Angular 2向后兼容。在Angular 2中开发的项目在Angular 4中没有任何问题。
现在让我们看看Angular 4中的新功能和更改。
为什么选择Angular4而不是Angular3?
Angular团队在内部遇到了一些版本问题和模块,由于冲突,他们不得不继续前进并发布下一版Angular - Angular4。
现在让我们看看Angular 4中添加的新功能 -
ngIf
Angular2仅支持if条件。 但是,Angular 4也支持if else条件。 让我们看一下使用ng-template的工作原理。
<span *ngIf="isavailable; else condition1">Condition is valid.</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
作为for循环中的关键字
在as关键字的帮助下as您可以存储如下所示的值 -
<div *ngFor="let i of months | slice:0:5 as total">
Months: {{i}} Total: {{total.length}}
</div>
变量total使用as关键字存储切片的输出。
动画包
Angular 4中的动画作为单独的包提供,需要从@ angular/animations导入。 在Angular2中,它可以使用@ angular/core 。 它的向后兼容性方面仍然保持不变。
Template
Angular 4使用《ng-template》作为标签而不是《template》; 后者用于Angular2。 Angular 4将《template》更改为《ng-template》的原因是《template》标签与html 《template》标准标签的名称冲突。 它将完全弃用。 这是Angular 4的主要变化之一。
TypeScript 2.2
Angular 4更新为最新版本的TypeScript,即2.2。 这有助于提高速度并在项目中提供更好的类型检查。
管道标题案例
Angular 4添加了一个新的管道标题案例,它将每个单词的第一个字母更改为大写。
<div>
<h2>{{ 'Angular 4 titlecase' | titlecase }}</h2>
</div>
上面的代码行生成以下输出 - Angular 4 Titlecase 。
Http搜索参数
搜索参数到http get api被简化了。 我们不需要像在Angular2中那样调用URLSearchParams。
更小更快的应用程序
与Angular2相比,Angular 4应用程序更小,更快。 它使用TypeScript 2.2版,这是最新版本,使最终编译的尺寸很小。
Angular 4 - Environment Setup
在本章中,我们将讨论Angular 4所需的环境设置。要安装Angular 4,我们需要以下内容 -
- Nodejs
- Npm
- Angular CLI
- 用于编写代码的IDE
Nodejs必须大于4,npm必须大于3。
Nodejs
要检查系统上是否安装了nodejs,请在终端中键入node –v 。 这将帮助您查看系统上当前安装的nodejs的版本。
C:\>node –v
v6.11.0
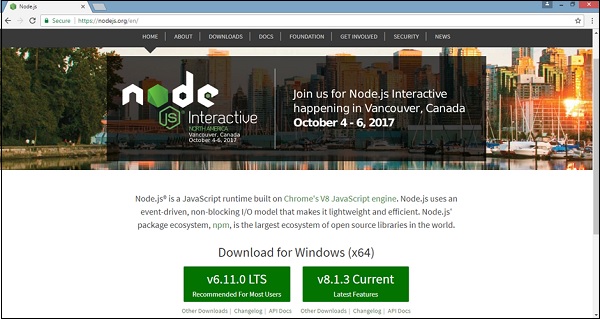
如果它没有打印任何内容,请在您的系统上安装nodejs。 要安装nodejs,请访问nodejs的主页https://nodejs.org/en/download/并根据您的操作系统安装软件包。
nodejs的主页将如下所示 -
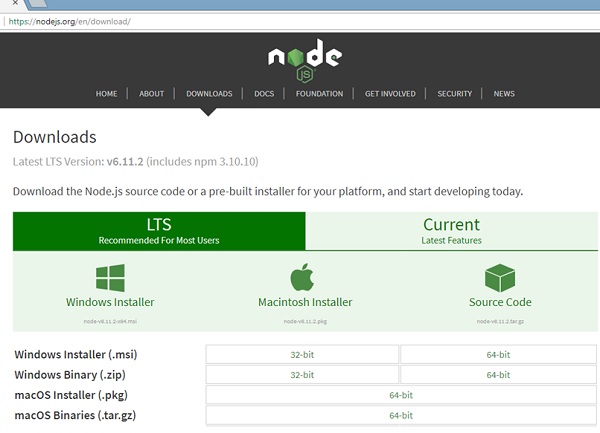
根据您的操作系统,安装所需的软件包。 一旦安装了nodejs,npm也将随之安装。 要检查是否安装了npm,请在终端中键入npm -v。 它应该显示npm的版本。
C:\>npm –v
5.3.0
在角度CLI的帮助下,Angular 4安装非常简单。 访问角度的主页https://cli.angular.io/以获取命令的参考。
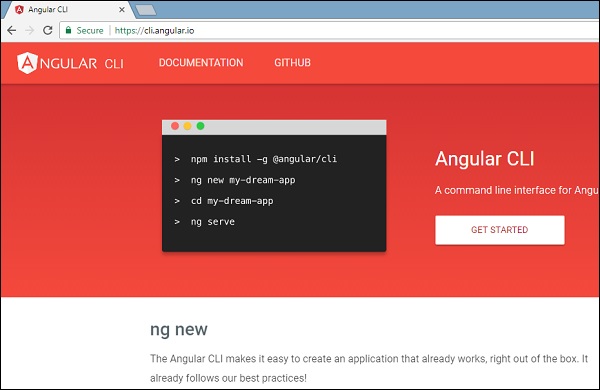
键入npm install –g @angular/cli ,在系统上安装angular cli。
安装Angular CLI后,您将在终端中获得上述安装。 您可以使用您选择的任何IDE,即WebStorm,Atom,Visual Studio Code等。
项目设置的细节将在下一章中介绍。
Angular 4 - Project Setup
AngularJS基于模型视图控制器,而Angular 2基于组件结构。 Angular 4与Angular2的结构相同,但与Angular2相比更快。
Angular4使用TypeScript 2.2版本,而Angular 2使用TypeScript版本1.8。 这给性能带来了很多不同。
为了安装Angular 4,Angular团队提出了Angular CLI,简化了安装。 您需要运行一些命令来安装Angular 4。
转到此站点https://cli.angular.io以安装Angular CLI。

要开始安装,我们首先需要确保我们安装了最新版本的nodejs和npm。 npm包与nodejs一起安装。
转到nodejs站点https://nodejs.org/en/ 。
建议用户使用最新版本的Nodejs v6.11.0。 已经拥有nodejs大于4的用户可以跳过上述过程。 安装nodejs后,您可以使用命令node –v检查命令行中的节点版本,如下所示 -
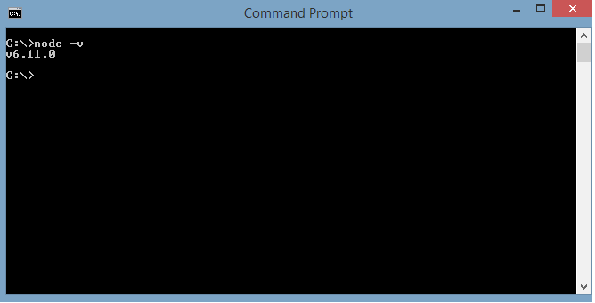
命令提示符显示v6.11.0。 一旦安装了nodejs,npm也将随之安装。
要检查npm的版本,请在终端中键入命令npm –v 。 它将显示npm的版本,如下所示。
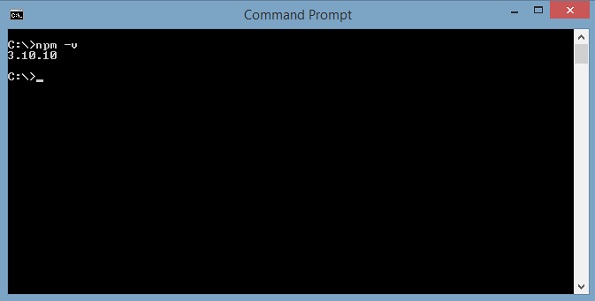
npm的版本是3.10.10。 现在我们已经安装了nodejs和npm,让我们运行angular cli命令来安装Angular 4.您将在网页上看到以下命令 -
npm install -g @angular/cli //command to install angular 4
ng new Angular 4-app // name of the project
cd my-dream-app
ng serve
让我们从命令行中的第一个命令开始,看看它是如何工作的。
首先,我们将创建一个空目录,其中,我们将运行Angular CLI命令。
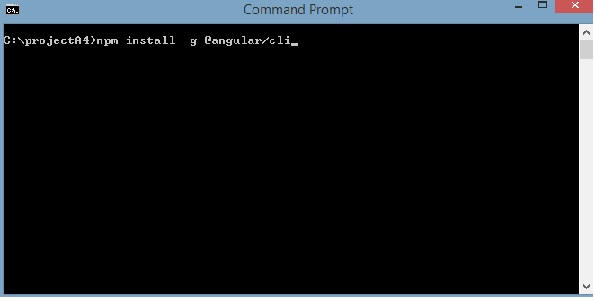
输入上面的命令来安装Angular 4.安装过程将开始,需要几分钟才能完成。
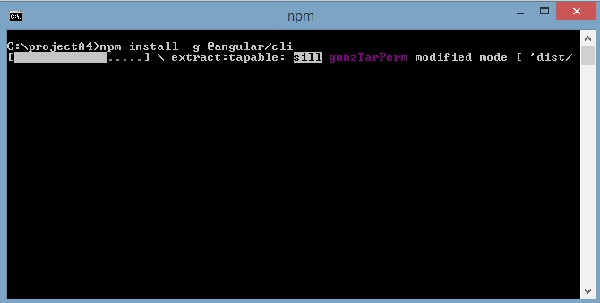
完成上述安装命令后,将显示以下命令提示符 -
我们创建了一个空文件夹ProjectA4并安装了Angular CLI命令。 我们还使用-g在全局安装Angular CLI。 现在,您可以在任何目录或文件夹中创建Angular 4项目,而不必安装Angular CLI项目,因为它全局安装在您的系统上,您可以从任何目录中使用它。
现在让我们检查是否安装了Angular CLI。 要检查安装,请在终端中运行以下命令 -
ng -v
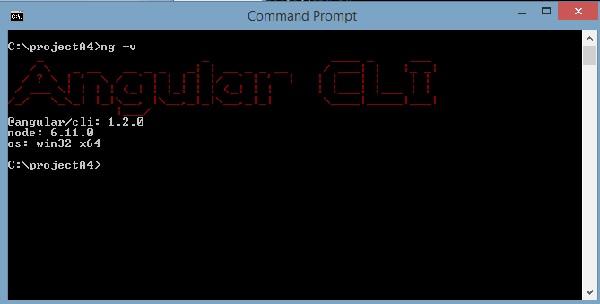
我们得到@ angular/cli版本,目前是1.2.0。 运行的节点版本是6.11.0以及操作系统详细信息。 以上细节告诉我们,我们已成功安装了角度cli,现在我们已准备好开始我们的项目。
我们现在安装了Angular 4.现在让我们在Angular 4中创建我们的第一个项目。要在Angular 4中创建项目,我们将使用以下命令 -
ng new projectname
我们将为ng new Angular 4-app命名该项目。
现在让我们在命令行中运行上面的命令。
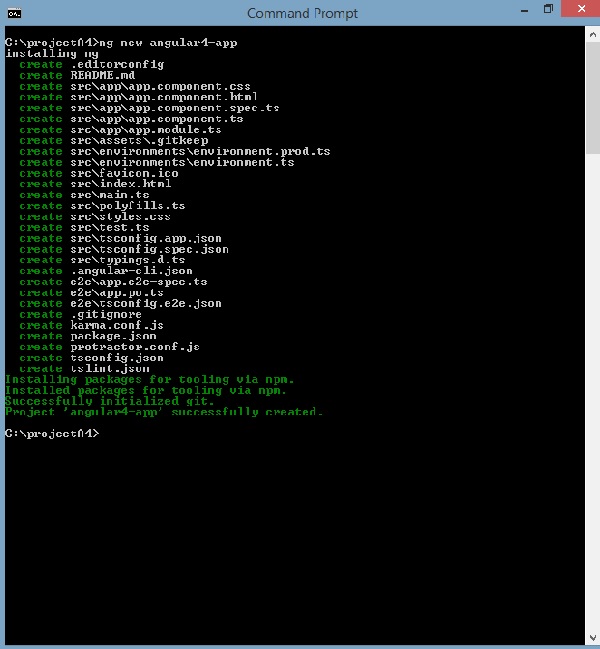
Angular 4-app项目已成功创建。 它安装了我们项目在Angular 4中运行所需的所有必需软件包。现在让我们切换到创建的项目,该项目位于Angular 4-app目录中。 在命令行中更改目录 - cd Angular 4-app 。
我们将使用Visual Studio Code IDE来处理Angular 4; 你可以使用任何IDE,即Atom,WebStorm等。
要下载Visual Studio Code,请访问https://code.visualstudio.com/并单击Download for Windows 。
单击“ Download for Windows以安装IDE并运行安装程序以开始使用IDE。
编辑器如下 -
我们还没有开始任何项目。 现在让我们使用angular-cli创建我们创建的项目。
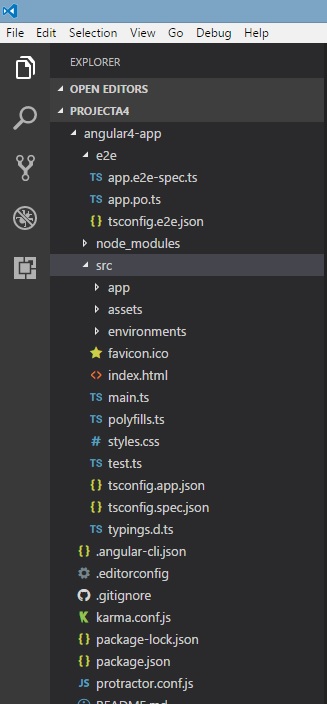
我们将考虑Angular 4-app项目。 让我们打开Angular 4-app,看看文件夹结构是怎样的。
现在我们有了项目的文件结构,让我们用以下命令编译我们的项目 -
ng serve
ng serve命令构建应用程序并启动Web服务器。
Web服务器在端口4200上启动。在浏览器中键入URL http://localhost:4200/并查看输出。 编译项目后,您将收到以下输出 -
在浏览器中运行http://localhost:4200/后,您将进入以下屏幕 -
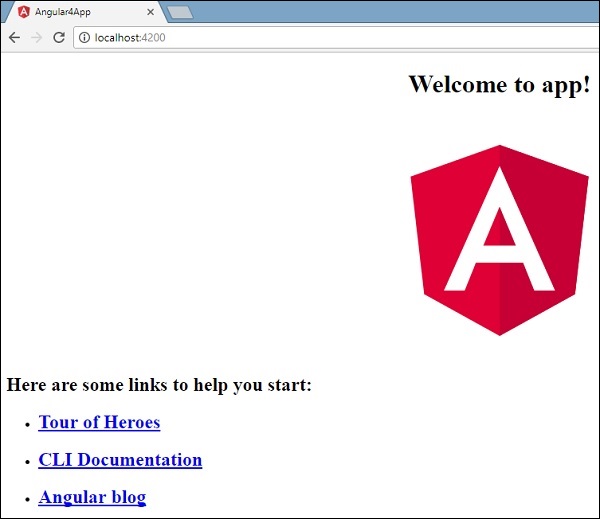
现在让我们进行一些更改以显示以下内容 -
“Welcome to Angular 4 project”
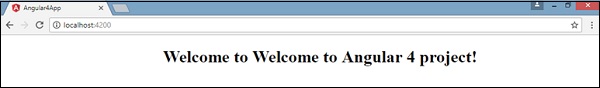
我们对文件进行了更改 - app.component.html和app.component.ts 。 我们将在随后的章节中讨论更多相关内容。
让我们完成项目设置。 如果你看到我们使用了端口4200,这是angular-cli在编译时使用的默认端口。 如果您希望使用以下命令,可以更改端口 -
ng serve --host 0.0.0.0 –port 4205
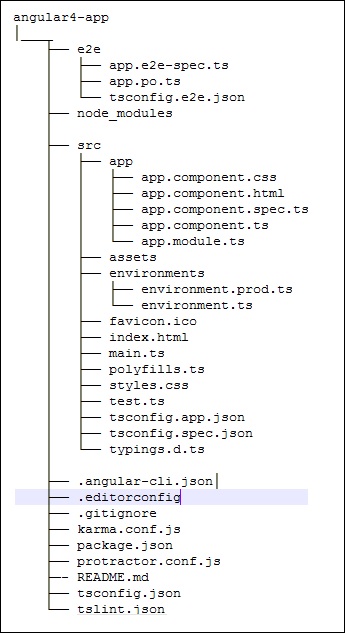
Angular 4 app文件夹具有以下folder structure -
e2e - 端到端测试文件夹。 主要是e2e用于集成测试,有助于确保应用程序正常运行。
node_modules - 安装的npm包是node_modules。 您可以打开文件夹并查看可用的包。
src - 这个文件夹是我们使用Angular 4处理项目的地方。
Angular 4 app文件夹具有以下file structure -
.angular-cli.json - 它基本上包含项目名称,cli版本等。
.editorconfig - 这是编辑器的配置文件。
.gitignore - 应将.gitignore文件提交到存储库中,以便与克隆存储库的任何其他用户共享忽略规则。
karma.conf.js - 用于通过量角器进行单元测试。 项目所需的所有信息都在karma.conf.js文件中提供。
package.json - package.json文件告诉你在运行npm install时将哪些库安装到node_modules中。
目前,如果您在编辑器中打开该文件,您将在其中添加以下模块。
"@angular/animations": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/common": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/compiler": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/core": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/forms": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/http": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/platform-browser": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/platform-browser-dynamic": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/router": "^4.0.0",
如果您需要添加更多库,可以在此处添加这些库并运行npm install命令。
protractor.conf.js - 这是应用程序所需的测试配置。
tsconfig.json - 这基本上包含编译期间所需的编译器选项。
tslint.json - 这是配置文件,其中包含编译时要考虑的规则。
src folder是主文件夹,它在internally has a different file structure 。
app
它包含下面描述的文件。 这些文件默认由angular-cli安装。
app.module.ts - 如果打开文件,您将看到代码引用了导入的不同库。 Angular-cli使用这些默认库进行导入 - 角度/核心,平台浏览器。 名称本身解释了库的用法。
它们被导入并保存到变量中,例如declarations, imports, providers和bootstrap 。
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
declarations - 在声明中,存储对组件的引用。 Appcomponent是每当启动新项目时创建的默认组件。 我们将学习如何在不同的部分创建新组件。
imports - 这将导入模块,如上所示。 目前,BrowserModule是从@ angular/platform-browser导入的导入的一部分。
providers - 这将引用创建的服务。 该服务将在后续章节中讨论。
bootstrap - 这引用了创建的默认组件,即AppComponent。
app.component.css - 您可以在此处编写css结构。 现在,我们已经为div添加了背景颜色,如下所示。
.divdetails{
background-color: #ccc;
}
app.component.html - html代码将在此文件中提供。
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div class = "divdetails">
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}!
</h1>
<img width = "300" src = "data:image/svg+xml;base64,PD94bWwgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4wIiBlbmNv
ZGluZz0idXRmLTgiPz4NCjwhLS0gR2VuZXJhdG9yOiBBZG9iZSBJbGx1c3RyYXRvciAxOS4xLjAsIFNWRyBFe
HBvcnQgUGx1Zy1JbiAuIFNWRyBWZXJzaW9uOiA2LjAwIEJ1aWxkIDApICAtLT4NCjxzdmcgdmVyc2lvbj0iMS4
xIiBpZD0iTGF5ZXJfMSIgeG1sbnM9Imh0dHA6Ly93d3cudzMub3JnLzIwMDAvc3ZnIiB4bWxuczp4bGluaz0iaH
R0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMTk5OS94bGluayIgeD0iMHB4IiB5PSIwcHgiDQoJIHZpZXdCb3g9IjAgMCAyNTAg
MjUwIiBzdHlsZT0iZW5hYmxlLWJhY2tncm91bmQ6bmV3IDAgMCAyNTAgMjUwOyIgeG1sOnNwYWNlPSJwcmVzZXJ2
ZSI+DQo8c3R5bGUgdHlwZT0idGV4dC9jc3MiPg0KCS5zdDB7ZmlsbDojREQwMDMxO30NCgkuc3Qxe2ZpbGw6I0M
zMDAyRjt9DQoJLnN0MntmaWxsOiNGRkZGRkY7fQ0KPC9zdHlsZT4NCjxnPg0KCTxwb2x5Z29uIGNsYXNzPSJzdD
AiIHBvaW50cz0iMTI1LDMwIDEyNSwzMCAxMjUsMzAgMzEuOSw2My4yIDQ2LjEsMTg2LjMgMTI1LDIzMCAxMjUsMj
MwIDEyNSwyMzAgMjAzLjksMTg2LjMgMjE4LjEsNjMuMiAJIi8+DQoJPHBvbHlnb24gY2xhc3M9InN0MSIgcG9pbn
RzPSIxMjUsMzAgMTI1LDUyLjIgMTI1LDUyLjEgMTI1LDE1My40IDEyNSwxNTMuNCAxMjUsMjMwIDEyNSwyMzAgMj
AzLjksMTg2LjMgMjE4LjEsNjMuMiAxMjUsMzAgCSIvPg0KCTxwYXRoIGNsYXNzPSJzdDIiIGQ9Ik0xMjUsNTIuMU
w2Ni44LDE4Mi42aDBoMjEuN2gwbDExLjctMjkuMmg0OS40bDExLjcsMjkuMmgwaDIxLjdoMEwxMjUsNTIuMUwxMj
UsNTIuMUwxMjUsNTIuMUwxMjUsNTIuMQ0KCQlMMTI1LDUyLjF6IE0xNDIsMTM1LjRIMTA4bDE3LTQwLjlMMTQyLD
EzNS40eiIvPg0KPC9nPg0KPC9zdmc+DQo=">
</div>
<h2>Here are some links to help you start: </h2>
<ul>
<li>
<h2>
<a target = "_blank" href="https://angular.io/tutorial">Tour of Heroes</a>
</h2>
</li>
<li>
<h2>
<a target = "_blank" href = "https://github.com/angular/angular-cli/wiki">
CLI Documentation
</a>
</h2>
</li>
<li>
<h2>
<a target="_blank" href="http://angularjs.blogspot.ca/">Angular blog</a>
</h2>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
这是项目创建时当前可用的默认html代码。
app.component.spec.ts - 这些是自动生成的文件,其中包含源组件的单元测试。
app.component.ts - 组件的类在此处定义。 您可以在.ts文件中处理html结构。 处理将包括诸如连接到数据库,与其他组件交互,路由,服务等活动。
该文件的结构如下 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'app';
}
Assets
您可以将图像,js文件保存在此文件夹中。
Environment
此文件夹包含生产环境或开发环境的详细信息。 该文件夹包含两个文件。
- environment.prod.ts
- environment.ts
这两个文件都详细说明了应该在生产环境还是开发环境中编译最终文件。
Angular 4 app文件夹的附加文件结构包括以下内容 -
favicon.ico
这是一个通常位于网站根目录中的文件。
的index.html
这是在浏览器中显示的文件。
<!doctype html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title>HTTP Search Param</title>
<base href = "/">
<link href = "https://fonts.googleapis.com/icon?family=Material+Icons" rel="stylesheet">
<link href = "https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Roboto|Roboto+Mono" rel="stylesheet">
<link href = "styles.c7c7b8bf22964ff954d3.bundle.css" rel="stylesheet">
<meta name = "viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel = "icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
</body>
</html>
正文有《app-root》《/app-root》 。 这是app.component.ts文件中使用的选择器,将显示app.component.html文件中的详细信息。
main.ts
main.ts是我们开始项目开发的文件。 首先导入我们需要的基本模块。 现在,如果您看到角度/核心,角度/平台浏览器动态,则在angular-cli安装和项目设置期间默认导入app.module和环境。
import { enableProdMode } from '@angular/core';
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from '@angular/platform-browser-dynamic';
import { AppModule } from './app/app.module';
import { environment } from './environments/environment';
if (environment.production) {
enableProdMode();
}
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule);
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule)具有父模块引用AppModule 。 因此,当它在浏览器中执行时,调用的文件是index.html。 Index.html内部引用调用父模块的main.ts,即执行以下代码时的AppModule -
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule);
当调用AppModule时,它会调用app.module.ts,它会根据boostrap进一步调用AppComponent,如下所示 -
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
在app.component.ts中,有一个selector: app-root ,用于index.html文件。 这将显示app.component.html中的内容。
以下内容将显示在浏览器中 -

polyfill.ts
这主要用于向后兼容。
styles.css
这是项目所需的样式文件。
test.ts
在这里,将处理用于测试项目的单元测试用例。
tsconfig.app.json
这在编译期间使用,它具有需要用于运行应用程序的配置详细信息。
tsconfig.spec.json
这有助于维护测试的详细信息。
typings.d.ts
它用于管理TypeScript定义。
最终的文件结构如下 -
Angular 4 - Components
Angular 4开发的主要部分是在组件中完成的。 组件基本上是与组件的.html文件交互的类,它们会显示在浏览器上。 我们在前面的章节中看到了文件结构。 文件结构具有应用程序组件,它包含以下文件 -
app.component.css
app.component.html
app.component.spec.ts
app.component.ts
app.module.ts
当我们使用angular-cli命令创建新项目时,默认情况下会创建上述文件。
如果你打开app.module.ts文件,它有一些导入的库,还有一个声明,分配appcomponent如下 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
声明包括我们已导入的AppComponent变量。 这成为父组件。
现在,angular-cli有一个命令来创建自己的组件。 但是,默认情况下创建的应用程序组件将始终保留为父组件,创建的下一个组件将构成子组件。
现在让我们运行命令来创建组件。
ng g component new-cmp
在命令行中运行上述命令时,您将收到以下输出 -
C:\projectA4\Angular 4-app>ng g component new-cmp
installing component
create src\app\new-cmp\new-cmp.component.css
create src\app\new-cmp\new-cmp.component.html
create src\app\new-cmp\new-cmp.component.spec.ts
create src\app\new-cmp\new-cmp.component.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
现在,如果我们去检查文件结构,我们将获得在src/app文件夹下创建的new-cmp新文件夹。
在new-cmp文件夹中创建以下文件 -
new-cmp.component.css - 创建新组件的css文件。
new-cmp.component.html - 创建了html文件。
new-cmp.component.spec.ts - 这可以用于单元测试。
new-cmp.component.ts - 在这里,我们可以定义模块,属性等。
更改将添加到app.module.ts文件中,如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
// includes the new-cmp component we created
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent // here it is added in declarations and will behave as a child component
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent] //for bootstrap the AppComponent the main app component is given.
})
export class AppModule { }
new-cmp.component.ts文件生成如下 -
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; // here angular/core is imported .
@Component({
// this is a declarator which starts with @ sign. The component word marked in bold needs to be the same.
selector: 'app-new-cmp', //
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
// reference to the html file created in the new component.
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css'] // reference to the style file.
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {}
}
如果你看到上面的new-cmp.component.ts文件,它会创建一个名为NewCmpComponent的新类,它实现OnInit.In,它有一个构造函数和一个名为ngOnInit()的方法。 执行类时,默认情况下会调用ngOnInit。
让我们检查一下流程是如何工作的。 现在,默认情况下创建的app组件将成为父组件。 稍后添加的任何组件都将成为子组件。
当我们点击http://localhost:4200/ browser中的url时,它首先执行index.html文件,如下所示 -
<!doctype html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "utf-8">
<title>Angular 4App</title>
<base href = "/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width = device-width, initial-scale = 1">
<link rel = "icon" type = "image/x-icon" href = "favicon.ico">
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
</body>
</html>
以上是普通的html文件,我们看不到浏览器中打印的任何内容。 看一下body部分的标签。
<app-root></app-root>
这是Angular默认创建的根标记。 此标记在main.ts文件中具有引用。
import { enableProdMode } from '@angular/core';
import { platformBrowserDynamic } from '@angular/platform-browser-dynamic';
import { AppModule } from './app/app.module';
import { environment } from './environments/environment';
if (environment.production) {
enableProdMode();
}
platformBrowserDynamic().bootstrapModule(AppModule);
AppModule是从主父模块的应用程序导入的,同样是给引导模块,这使得appmodule加载。
现在让我们看看app.module.ts文件 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
这里,AppComponent是给定的名称,即存储app. Component.ts引用的变量app. Component.ts app. Component.ts和相同的内容被赋予bootstrap。 现在让我们看看app.component.ts文件。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
}
Angular core被导入并称为Component,并且在Declarator中使用相同的 -
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
在声明符对选择器的styleUrl中,给出了templateUrl和styleUrl 。 这里的选择器只是放在我们上面看到的index.html文件中的标记。
AppComponent类有一个名为title的变量,它在浏览器中显示。
@Component使用名为app.component.html的templateUrl,如下所示 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
它只有html代码和大括号中的变量标题。 它将替换为app.component.ts文件中的值。 这称为绑定。 我们将在后续章节中讨论绑定的概念。
现在我们已经创建了一个名为new-cmp的新组件。 当运行用于创建新组件的命令时, app.module.ts文件中包含相同的内容。
app.module.ts引用了创建的新组件。
现在让我们检查在new-cmp中创建的新文件。
new-cmp.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-new-cmp',
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css']
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {}
}
在这里,我们也必须导入核心。 组件的引用在声明符中使用。
声明器具有名为app-new-cmp的选择器以及templateUrl和styleUrl 。
名为new-cmp.component.html的.html如下 -
<p>
new-cmp works!
</p>
如上所示,我们有html代码,即p标签。 样式文件为空,因为我们目前不需要任何样式。 但是当我们运行项目时,我们看不到任何与新组件相关的内容在浏览器中显示。 现在让我们添加一些内容,稍后可以在浏览器中看到相同内容。
选择器,即app-new-cmp需要添加到app.component .html文件中,如下所示 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<app-new-cmp></app-new-cmp>
添加《app-new-cmp》《/app-new-cmp》标记后,创建的新组件的.html文件中的所有内容都将与父组件数据一起显示在浏览器中。
让我们看一下new component .html文件和new-cmp.component.ts文件。
new-cmp.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-new-cmp',
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css']
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
newcomponent = "Entered in new component created";
constructor() {}
ngOnInit() { }
}
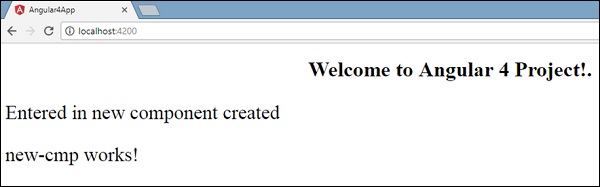
在类中,我们添加了一个名为new component的变量,其值为“ Entered in new component created ”。
上述变量绑定在.new-cmp.component.html文件中,如下所示 -
<p>
{{newcomponent}}
</p>
<p>
new-cmp works!
</p>
现在,因为我们在《app-new-cmp》《/app-new-cmp》包含了《app-new-cmp》《/app-new-cmp》选择器app. component .html app. component .html是父组件的.html,新组件.html文件(new-cmp.component.html)中的内容在浏览器上显示如下 -
同样,我们可以根据我们的要求使用app.component.html文件中的选择器创建组件并进行链接。
Angular 4 - Module
Angular中的Module是指您可以对与应用程序相关的组件,指令,管道和服务进行分组的位置。
如果您正在开发网站,页眉,页脚,左侧,中间和右侧部分将成为模块的一部分。
要定义模块,我们可以使用NgModule 。 使用Angular -cli命令创建新项目时,默认情况下会在app.module.ts文件中创建ngmodule,其外观如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
NgModule需要按如下方式导入 -
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
ngmodule的结构如下所示 -
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
它以@NgModule ,包含一个具有声明,导入,提供程序和引导程序的对象。
宣言(Declaration)
它是一组创建的组件。 如果创建了任何新组件,它将首先导入,并且引用将包含在声明中,如下所示 -
declarations: [
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent
]
Import
它是应用程序中需要使用的一组模块。 它也可以由Declaration数组中的组件使用。 例如,现在在@NgModule中我们看到导入的浏览器模块。 如果您的应用程序需要表单,您可以按如下方式包含该模块 -
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
@NgModule的导入将如下所示 -
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule
]
提供商(Providers)
这将包括创建的服务。
Bootstrap
这包括用于开始执行的主app组件。
Angular 4 - Data Binding
数据绑定可以从AngularJS,Angular 2获得,现在也可以在Angular 4中使用。 我们使用花括号进行数据绑定 - {{}}; 这个过程叫做插值。 我们在前面的例子中已经看到我们如何向变量标题声明值,并在浏览器中打印相同的值。
app.component.html文件中的变量称为{{title}},并且在app.component.ts文件和app.component.html初始化title的值,将显示该值。
现在让我们在浏览器中创建一个月下拉列表。 为此,我们在app.component.ts创建了一个月数组,如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
// declared array of months.
months = ["January", "Feburary", "March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
}
上面显示的月份数组将显示在浏览器的下拉列表中。 为此,我们将使用以下代码行 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced. -->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select>
<option *ngFor="let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
我们已经创建了带选项的普通选择标记。 在选项中,我们使用了for loop 。 for loop用于遍历月份数组,这反过来将创建具有月份中存在的值的选项标记。
Angular的语法是*ngFor = “let I of months”并获得我们在{{i}}中显示月份的值。
两个花括号有助于数据绑定。 您在app.component.ts文件中声明变量,并使用大括号替换相同的变量。
让我们在浏览器中看到上个月数组的输出
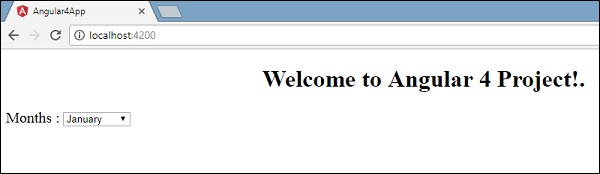
app.component.ts设置的变量可以使用大括号与app.component.html绑定; 例如, {{}} 。
现在让我们根据条件在浏览器中显示数据。 在这里,我们添加了一个变量并将值赋值为true。 使用if语句,我们可以隐藏/显示要显示的内容。
例子 (Example)
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = true; //variable is set to true
}
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select>
<option *ngFor = "let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf = "isavailable">Condition is valid.</span>
//over here based on if condition the text condition is valid is displayed.
If the value of isavailable is set to false it will not display the text.
</div>
输出 (Output)
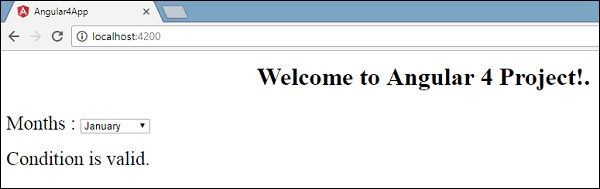
让我们使用IF THEN ELSE条件尝试上面的例子。
例子 (Example)
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = false;
}
在这种情况下,我们将isavailable变量设为false。 要打印else条件,我们必须创建ng-template ,如下所示 -
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
完整的代码看起来像这样 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select>
<option *ngFor="let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf="isavailable; else condition1">Condition is valid.</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
</div>
If与else条件一起使用,则使用的变量是condition1 。 将相同内容指定为ng-template的id ,当可用变量设置为false时,将显示文本Condition is invalid 。
以下屏幕截图显示了浏览器中的显示。
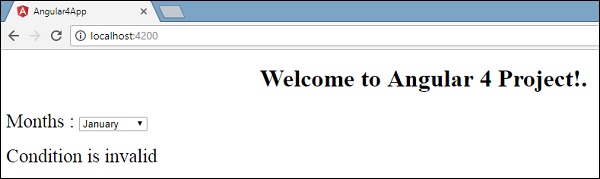
现在让我们使用if then else条件。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = true;
}
现在,我们将变量isavailable为true。 在html中,条件以下列方式编写 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style="text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select>
<option *ngFor="let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf="isavailable; then condition1 else condition2">Condition is valid.</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
</div>
如果变量为true,则为condition1 ,否则为condition2 。 现在,使用id #condition1和#condition2创建两个模板。
浏览器中的显示如下 -
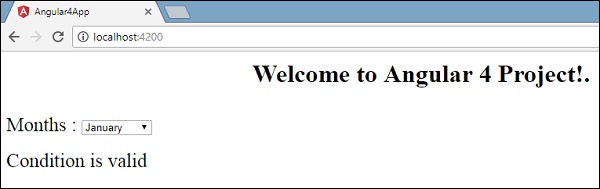
Angular 4 - Event Binding
在本章中,我们将讨论事件绑定如何在Angular 4中工作。当用户以键盘移动,鼠标单击或鼠标悬停的形式与应用程序交互时,它会生成一个事件。 需要处理这些事件以执行某种操作。 这是事件绑定的结果。
让我们考虑一个更好地理解这一点的例子。
app.component.html
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select>
<option *ngFor = "let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf = "isavailable; then condition1 else condition2">
Condition is valid.
</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
</div>
<button (click)="myClickFunction($event)">
Click Me
</button>
在app.component.html文件中,我们定义了一个按钮,并使用click事件向其添加了一个函数。
以下是定义按钮并向其添加功能的语法。
(click)="myClickFunction($event)"
该函数在.ts文件中定义: app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "Feburary", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = true;
myClickFunction(event) {
//just added console.log which will display the event details in browser on click of the button.
alert("Button is clicked");
console.log(event);
}
}
单击按钮后,控件将进入myClickFunction功能,并出现一个对话框,其中显示the Button is clicked ,如下面的屏幕截图所示 -

现在让我们将更改事件添加到下拉列表中。
以下代码行将帮助您将更改事件添加到下拉列表中 -
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select (change) = "changemonths($event)">
<option *ngFor = "let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf = "isavailable; then condition1 else condition2">
Condition is valid.
</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid</ng-template>
</div>
<button (click) = "myClickFunction($event)">Click Me</button>
该函数在app.component.ts文件中声明 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "Feburary", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = true;
myClickFunction(event) {
alert("Button is clicked");
console.log(event);
}
changemonths(event) {
console.log("Changed month from the Dropdown");
console.log(event);
}
}
控制台消息“ Changed month from the Dropdown ”将与事件一起显示在控制台中。
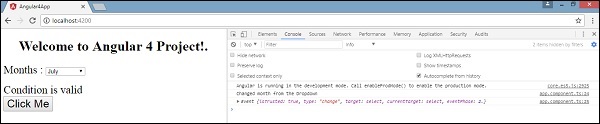
当下拉列表中的值发生变化时,让我们在app.component.ts添加一条警告消息,如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = true;
myClickFunction(event) {
//just added console.log which will display the event details in browser
on click of the button.
alert("Button is clicked");
console.log(event);
}
changemonths(event) {
alert("Changed month from the Dropdown");
}
}
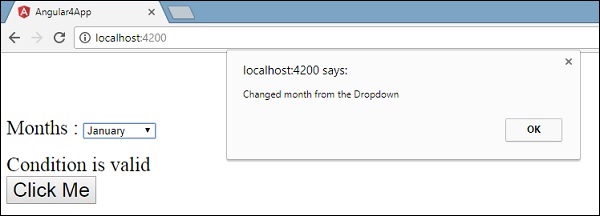
当下拉列表中的值更改时,将出现一个对话框,并显示以下消息 - “ Changed month from the Dropdown ”。
Angular 4 - Templates
Angular 4使用《ng-template》作为标签,而不是Angular2中使用的《template》 。 Angular 4将《template》更改为《ng-template》的原因是因为《template》标记与html 《template》标准标记之间存在名称冲突。 它将完全弃用。 这是Angular 4的主要变化之一。
现在让我们使用模板和if else条件并查看输出。
app.component.html
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select (change) = "changemonths($event)" name = "month">
<option *ngFor = "let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf = "isavailable;then condition1 else condition2">Condition is valid.</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid from template</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid from template</ng-template>
</div>
<button (click) = "myClickFunction($event)">Click Me</button>
对于Span标记,我们添加了带有else条件的if语句,并将调用模板condition1,否则为condition2。
模板的调用方式如下 -
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid from template</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid from template</ng-template>
如果条件为真,则调用condition1模板,否则调用condition2。
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
//array of months.
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April",
"May", "June", "July", "August", "September",
"October", "November", "December"];
isavailable = false;
myClickFunction(event) {
this.isavailable = false;
}
changemonths(event) {
alert("Changed month from the Dropdown");
console.log(event);
}
}
浏览器中的输出如下 -
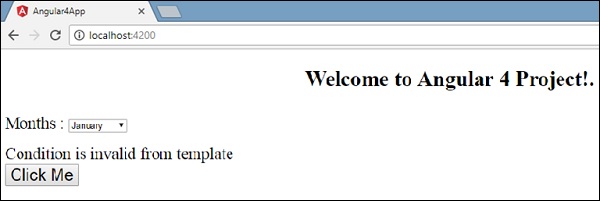
变量isavailable为false,因此打印出condition2模板。 如果单击该按钮,将调用相应的模板。 如果您检查浏览器,您将看到永远不会在dom中获得span标记。 以下示例将帮助您理解相同的内容。
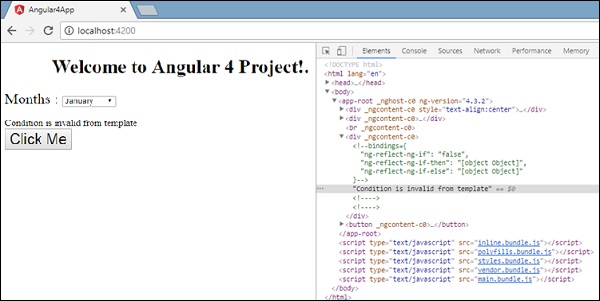
如果您检查浏览器,您将看到dom没有span标记。 它具有Condition is invalid from template在dom中的Condition is invalid from template 。
html中的以下代码行将帮助我们在dom中获取span标记。
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "text-align:center">
<h1>
Welcome to {{title}}.
</h1>
</div>
<div> Months :
<select (change) = "changemonths($event)" name = "month">
<option *ngFor = "let i of months">{{i}}</option>
</select>
</div>
<br/>
<div>
<span *ngIf = "isavailable; else condition2">Condition is valid.</span>
<ng-template #condition1>Condition is valid from template</ng-template>
<ng-template #condition2>Condition is invalid from template</ng-template>
</div>
<button (click)="myClickFunction($event)">Click Me</button>
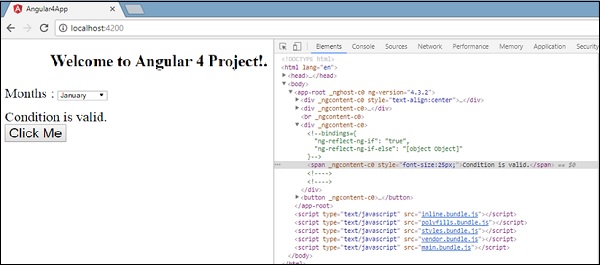
如果我们删除then条件,我们在浏览器中得到“Condition is valid”消息,并且dom中也可以使用span标记。 例如,在app.component.ts ,我们将app.component.ts变量设为true。
Angular 4 - Directives
Angular中的Directives是一个js类,它被声明为@directive 。 我们在Angular中有3个指令。 指令如下 -
组件指令
这些构成了主类,其中详细说明了如何在运行时处理,实例化和使用组件。
结构指令
结构指令主要处理操作dom元素。 结构指令在指令之前有*符号。 例如, *ngIf和*ngFor 。
属性指令
属性指令涉及更改dom元素的外观和行为。 您可以创建自己的指令,如下所示。
如何创建自定义指令?
在本节中,我们将讨论要在组件中使用的自定义指令。 自定义指令由我们创建,不是标准的。
让我们看看如何创建自定义指令。 我们将使用命令行创建指令。 使用命令行创建指令的命令是 -
ng g directive nameofthedirective
e.g
ng g directive changeText
这就是它在命令行中的显示方式
C:\projectA4\Angular 4-app>ng g directive changeText
installing directive
create src\app\change-text.directive.spec.ts
create src\app\change-text.directive.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
创建上述文件,即change-text.directive.spec.ts和change-text.directive.ts并更新app.module.ts文件。
app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
ChangeTextDirective类包含在上述文件的声明中。 该类也是从下面给出的文件中导入的。
change-text. directive
import { Directive } from '@angular/core';
@Directive({
selector: '[changeText]'
})
export class ChangeTextDirective {
constructor() { }
}
上面的文件有一个指令,它还有一个selector属性。 无论我们在选择器中定义什么,都必须在视图中匹配,我们在其中分配自定义指令。
在app.component.html视图中,让我们添加如下指令 -
<div style="text-align:center">
<span changeText >Welcome to {{title}}.</span>
</div>
我们将在change-text.directive.ts文件中编写更改,如下所示 -
change-text.directive.ts
import { Directive, ElementRef} from '@angular/core';
@Directive({
selector: '[changeText]'
})
export class ChangeTextDirective {
constructor(Element: ElementRef) {
console.log(Element);
Element.nativeElement.innerText="Text is changed by changeText Directive. ";
}
}
在上面的文件中,有一个名为ChangeTextDirective的类和一个构造函数,它采用ElementRef类型的元素,这是必需的。 该元素包含应用Change Text指令的所有详细信息。
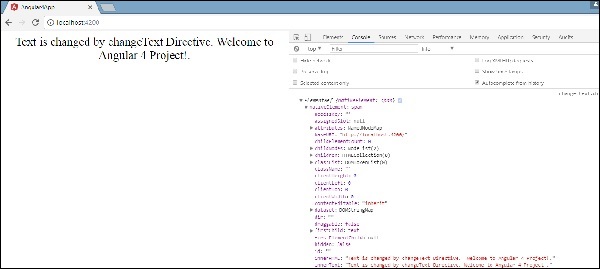
我们添加了console.log元素。 可以在浏览器控制台中看到相同的输出。 元素的文本也如上所示进行了更改。
现在,浏览器将显示以下内容。
Angular 4 - Pipes
在本章中,我们将讨论什么是Angular 4中的管道。管道在Angular1中早先称为过滤器,在Angular 2和4中称为管道。
| character用于转换数据。 以下是相同的语法
{{ Welcome to Angular 4 | lowercase}}
它将整数,字符串,数组和日期作为输入用|分隔 按要求格式转换,并在浏览器中显示相同的格式。
让我们考虑一些使用管道的例子。
在这里,我们想要显示给大写的文本。 这可以使用管道完成,如下所示 -
在app.component.ts文件中,我们定义了title变量 -
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
}
以下代码行进入app.component.html文件。
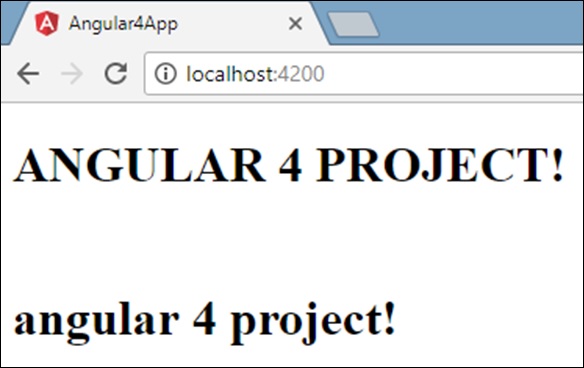
<b>{{title | uppercase}}</b><br/>
<b>{{title | lowercase}}</b>
浏览器显示如下面的屏幕截图所示 -
Angular 4提供了一些内置管道。 管道列在下面 -
- Lowercasepipe
- Uppercasepipe
- Datepipe
- Currencypipe
- Jsonpipe
- Percentpipe
- Decimalpipe
- Slicepipe
我们已经看到了小写和大写的管道。 现在让我们看看其他管道是如何工作的。
以下代码行将帮助我们在app.component.ts文件中定义所需的变量 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate = new Date();
jsonval = {name:'Rox', age:'25', address:{a1:'Mumbai', a2:'Karnataka'}};
months = ["Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "April", "May", "Jun",
"July", "Aug", "Sept", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"];
}
我们将使用app.component.html文件中的管道。
<!--The content below is only a placeholder and can be replaced.-->
<div style = "width:100%;">
<div style = "width:40%;float:left;border:solid 1px black;">
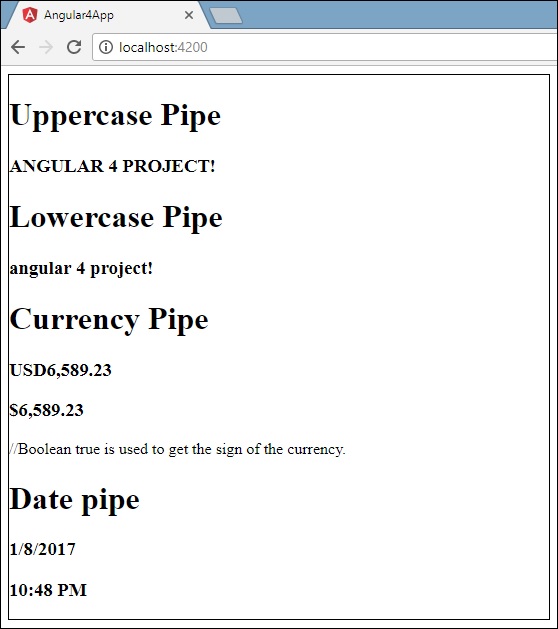
<h1>Uppercase Pipe</h1>
<b>{{title | uppercase}}</b><br/>
<h1>Lowercase Pipe</h1>
<b>{{title | lowercase}}</b>
<h1>Currency Pipe</h1>
<b>{{6589.23 | currency:"USD"}}</b><br/>
<b>{{6589.23 | currency:"USD":true}}</b> //Boolean true is used to get the sign of the currency.
<h1>Date pipe</h1>
<b>{{todaydate | date:'d/M/y'}}</b><br/>
<b>{{todaydate | date:'shortTime'}}</b>
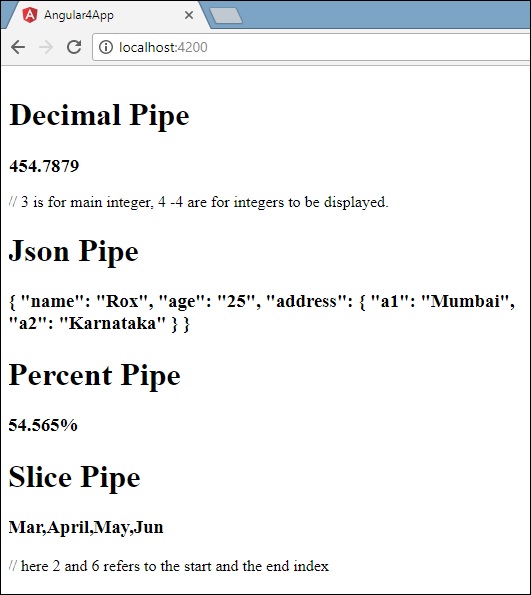
<h1>Decimal Pipe</h1>
<b>{{ 454.78787814 | number: '3.4-4' }}</b> // 3 is for main integer, 4 -4 are for integers to be displayed.
</div>
<div style = "width:40%;float:left;border:solid 1px black;">
<h1>Json Pipe</h1>
<b>{{ jsonval | json }}</b>
<h1>Percent Pipe</h1>
<b>{{00.54565 | percent}}</b>
<h1>Slice Pipe</h1>
<b>{{months | slice:2:6}}</b>
// here 2 and 6 refers to the start and the end index
</div>
</div>
以下屏幕截图显示了每个管道的输出 -
如何创建自定义管道?
为了创建自定义管道,我们创建了一个新的ts文件。 在这里,我们要创建sqrt自定义管道。 我们给文件命名相同,它看起来如下 -
app.sqrt.ts
import {Pipe, PipeTransform} from '@angular/core';
@Pipe ({
name : 'sqrt'
})
export class SqrtPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(val : number) : number {
return Math.sqrt(val);
}
}
要创建自定义管道,我们必须从Angular/core导入管道和管道转换。 在@Pipe指令中,我们必须为管道命名,该管道将在我们的.html文件中使用。 因为,我们正在创建sqrt管道,我们将其命名为sqrt。
随着我们继续前进,我们必须创建类,类名称是SqrtPipe 。 该类将实现PipeTransform 。
类中定义的transform方法将参数作为数字,并在取平方根后返回数字。
由于我们已经创建了一个新文件,我们需要在app.module.ts.添加相同的app.module.ts. 这样做如下 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
import { SqrtPipe } from './app.sqrt';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
SqrtPipe,
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
我们创建了app.sqrt.ts类。 我们必须在app.module.ts导入相同app.module.ts并指定文件的路径。 它也必须包含在声明中,如上所示。
现在让我们看一下app.component.html文件中对sqrt管道的app.component.html 。
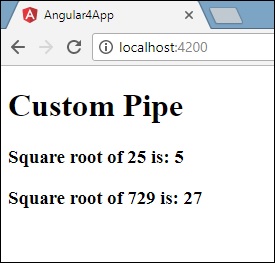
<h1>Custom Pipe</h1>
<b>Square root of 25 is: {{25 | sqrt}}</b>
<br/>
<b>Square root of 729 is: {{729 | sqrt}}</b>
输出如下 -
Angular 4 - Routing
路由基本上意味着在页面之间导航。 您已经看到许多链接指向新页面的网站。 这可以使用路由来实现。 这里我们引用的页面将采用组件的形式。 我们已经看到了如何创建组件。 现在让我们创建一个组件,看看如何使用它进行路由。
在主要的父组件app.module.ts ,我们现在必须包含路由器模块,如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule} from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
import { SqrtPipe } from './app.sqrt';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
SqrtPipe,
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'new-cmp',
component: NewCmpComponent
}
])
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
从'@ angular/router'导入{RouterModule}
这里,RouterModule是从angular/router导入的。 该模块包含在导入中,如下所示 -
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'new-cmp',
component: NewCmpComponent
}
])
RouterModule引用forRoot ,它将输入作为数组,而数组又包含路径和组件的对象。 Path是路由器的名称,component是类的名称,即创建的组件。
现在让我们看一下组件创建的文件 -
新cmp.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-new-cmp',
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css']
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
newcomponent = "Entered in new component created";
constructor() {}
ngOnInit() { }
}
主模块的导入中提到了突出显示的类。
New-cmp.component.html
<p>
{{newcomponent}}
</p>
<p>
new-cmp works!
</p>
现在,我们需要html文件中的上述内容,只要需要或从主模块中单击即可显示。 为此,我们需要在app.component.html添加路由器详细信息。
<h1>Custom Pipe</h1>
<b>Square root of 25 is: {{25 | sqrt}}</b><br/>
<b>Square root of 729 is: {{729 | sqrt}}</b>
<br />
<br />
<br />
<a routerLink = "new-cmp">New component</a>
<br />
<br/>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
在上面的代码中,我们创建了锚链接标记,并将routerLink作为“new-cmp” 。 这在app.module.ts称为路径。
当用户单击new component ,该页面应显示该内容。 为此,我们需要以下标签 - 《router-outlet》 《/router-outlet》 。
上述标记可确保当用户单击new component时, new-cmp.component.html中的内容将显示在页面上。
现在让我们看看输出如何在浏览器上显示。
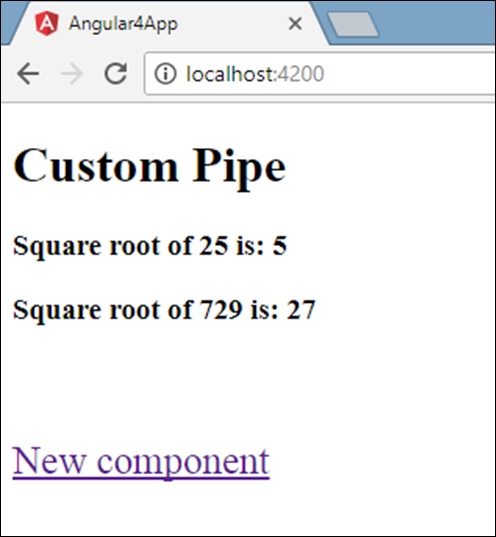
当用户单击“新建组件”时,您将在浏览器中看到以下内容。

该网址包含http://localhost:4200/new-cmp 。 这里,new-cmp被附加到原始url,这是app.module.ts给出的路径和app.module.ts的router-link。
当用户单击“新建”组件时,页面不会刷新,并且内容将显示给用户而不进行任何重新加载。 单击时,只会重新加载特定的站点代码。 当我们在页面上有大量内容并且需要根据用户交互加载时,此功能会有所帮助。 该功能还可以提供良好的用户体验,因为页面未重新加载。
Angular 4 - Services
在本章中,我们将讨论Angular 4中的服务。
我们可能会遇到需要在页面的任何位置使用某些代码的情况。 它可以用于需要跨组件共享的数据连接等。服务可以帮助我们实现这一目标。 通过服务,我们可以访问整个项目中其他组件的方法和属性。
要创建服务,我们需要使用命令行。 同样的命令是 -
C:\projectA4\Angular 4-app>ng g service myservice
installing service
create src\app\myservice.service.spec.ts
create src\app\myservice.service.ts
WARNING Service is generated but not provided, it must be provided to be used
C:\projectA4\Angular 4-app>
文件在app文件夹中创建如下 -
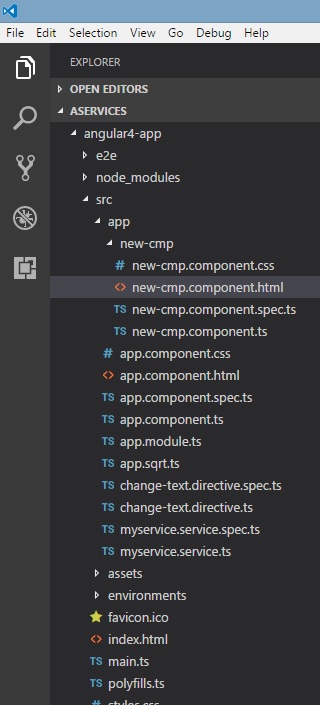
以下是在底部创建的文件 - myservice.service.specs.ts和myservice.service.ts 。
myservice.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class MyserviceService {
constructor() { }
}
这里,Injectable模块是从@angular/core导入的。 它包含@Injectable方法和一个名为MyserviceService的类。 我们将在这个类中创建我们的服务功能。
在创建新服务之前,我们需要包含在主父app.module.ts创建的服务。
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule} from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
import { SqrtPipe } from './app.sqrt';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
SqrtPipe,
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'new-cmp',
component: NewCmpComponent
}
])
],
providers: [MyserviceService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
我们使用类名导入了Service,并在提供程序中使用了相同的类。 现在让我们切换回服务类并创建一个服务功能。
在服务类中,我们将创建一个显示今天日期的函数。 我们可以在主要父组件app.component.ts使用相同的函数,也可以在我们在new-cmp.component.ts中创建的新组件new-cmp.component.ts中使用相同的函数。
现在让我们看看该函数在服务中的外观以及如何在组件中使用它。
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class MyserviceService {
constructor() { }
showTodayDate() {
let ndate = new Date();
return ndate;
}
}
在上面的服务文件中,我们创建了一个函数showTodayDate 。 现在我们将返回创建的新Date()。 让我们看看如何在组件类中访问此函数。
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
}
}
默认情况下,在创建的任何组件中都会调用ngOnInit函数。 如上所示,从服务中获取日期。 要获取服务的更多详细信息,我们需要首先在组件ts文件中包含该服务。
我们将在.html文件中显示日期,如下所示 -
{{todaydate}}
<app-new-cmp></app-new-cmp>
// data to be displayed to user from the new component class.
现在让我们看看如何在创建的新组件中使用该服务。
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './../myservice.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-new-cmp',
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css']
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
todaydate;
newcomponent = "Entered in new component created";
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
}
}
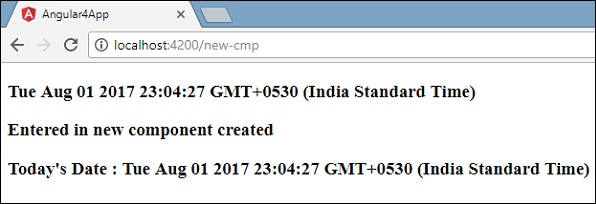
在我们创建的新组件中,我们需要首先导入我们想要的服务并访问它们的方法和属性。 请参阅突出显示的代码。 todaydate显示在组件html中,如下所示 -
<p>
{{newcomponent}}
</p>
<p>
Today's Date : {{todaydate}}
</p>
新组件的选择器在app.component.html文件中使用。 上述html文件中的内容将显示在浏览器中,如下所示 -
如果在任何组件中更改服务的属性,则在其他组件中也会更改相同的属性。 现在让我们看看它是如何工作的。
我们将在服务中定义一个变量,并在父组件和新组件中使用它。 我们将再次更改父组件中的属性,并查看是否在新组件中更改了相同的属性。
在myservice.service.ts ,我们创建了一个属性,并在其他父组件和新组件中使用了相同的属性。
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class MyserviceService {
serviceproperty = "Service Created";
constructor() { }
showTodayDate() {
let ndate = new Date();
return ndate;
}
}
现在让我们在其他组件中使用serviceproperty变量。 在app.component.ts ,我们正在访问变量,如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
componentproperty;
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
console.log(this.myservice.serviceproperty);
this.myservice.serviceproperty = "component created"; // value is changed.
this.componentproperty = this.myservice.serviceproperty;
}
}
我们现在将获取变量并在console.log上工作。 在下一行中,我们将变量的值更改为“ component created ”。 我们将在new-cmp.component.ts执行相同new-cmp.component.ts 。
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './../myservice.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-new-cmp',
templateUrl: './new-cmp.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./new-cmp.component.css']
})
export class NewCmpComponent implements OnInit {
todaydate;
newcomponentproperty;
newcomponent = "Entered in newcomponent";
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
this.newcomponentproperty = this.myservice.serviceproperty;
}
}
在上面的组件中,我们不会更改任何内容,只是直接将属性分配给组件属性。
现在,当您在浏览器中执行它时,将更改服务属性,因为它的值在app.component.ts更改,并且将显示new-cmp.component.ts的相同new-cmp.component.ts 。
在更改之前,还要检查控制台中的值。
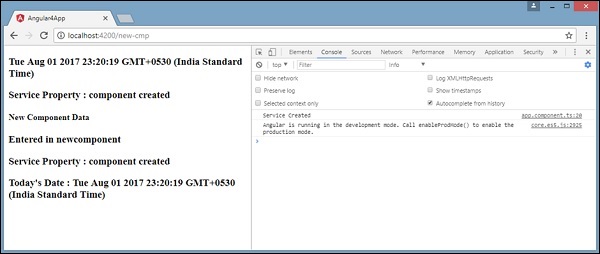
Angular 4 - Http Service
Http Service将帮助我们获取外部数据,发布到它等。我们需要导入http模块以使用http服务。 让我们考虑一个例子来了解如何使用http服务。
要开始使用http服务,我们需要在app.module.ts导入模块,如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
HttpModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
如果你看到突出显示的代码,我们从@ angular/http导入了HttpModule,并且在imports数组中也添加了相同的内容。
现在让我们在app.component.ts使用http服务。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private http: Http) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.http.get("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users").
map((response) ⇒ response.json()).
subscribe((data) ⇒ console.log(data))
}
}
让我们理解上面突出显示的代码。 我们需要导入http以使用该服务,其操作如下 -
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
在AppComponent类中,创建了一个构造函数,并且私有变量http的类型为Http。 要获取数据,我们需要使用http提供的get API ,如下所示
this.http.get();
它将获取url作为参数,如代码中所示。
我们将使用测试网址 - https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users来获取json数据。 对获取的url数据映射执行两个操作并进行订阅。 Map方法有助于将数据转换为json格式。 要使用地图,我们需要导入相同的内容,如下所示 -
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
完成映射后,订阅将在控制台中记录输出,如浏览器所示 -
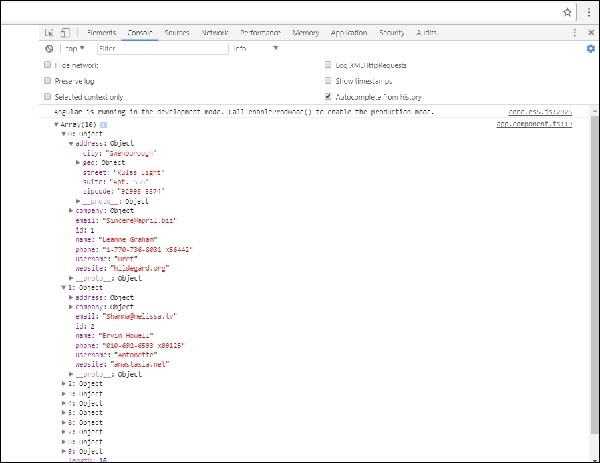
如果看到,json对象将显示在控制台中。 对象也可以在浏览器中显示。
对于要在浏览器中显示的对象,请更新app.component.html和app.component.ts的代码,如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private http: Http) { }
httpdata;
ngOnInit() {
this.http.get("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users").
map(
(response) ⇒ response.json()
).
subscribe(
(data) ⇒ {this.displaydata(data);}
)
}
displaydata(data) {this.httpdata = data;}
}
在app.component.ts ,使用subscribe方法,我们将调用display data方法并将作为参数获取的数据传递给它。
在显示数据方法中,我们将数据存储在变量httpdata中。 数据显示在浏览器中, for覆盖此httpdata变量,该变量在app.component.html文件中完成。
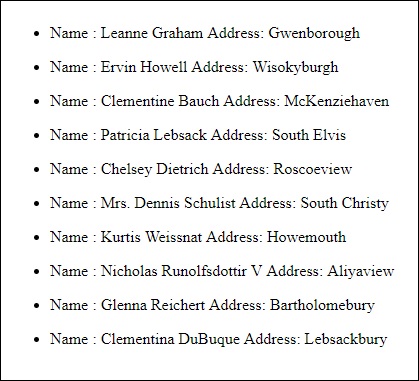
<ul *ngFor = "let data of httpdata">
<li>Name : {{data.name}} Address: {{data.address.city}}</li>
</ul>
json对象如下 -
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Leanne Graham",
"username": "Bret",
"email": "Sincere@april.biz",
"address": {
"street": "Kulas Light",
"suite": "Apt. 556",
"city": "Gwenborough",
"zipcode": "92998-3874",
"geo": {
"lat": "-37.3159",
"lng": "81.1496"
}
},
"phone": "1-770-736-8031 x56442",
"website": "hildegard.org",
"company": {
"name": "Romaguera-Crona",
"catchPhrase": "Multi-layered client-server neural-net",
"bs": "harness real-time e-markets"
}
}
该对象具有内部具有街道,城市等的id,名称,用户名,电子邮件和地址等属性以及与电话,网站和公司相关的其他详细信息。 使用for循环,我们将在浏览器中显示名称和城市详细信息,如app.component.html文件中所示。
这是显示器在浏览器中的显示方式 -
现在让我们添加搜索参数,该参数将根据特定数据进行过滤。 我们需要根据传递的搜索参数获取数据。
以下是app.component.html和app.component.ts文件中所做的更改 -
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'app';
searchparam = 2;
jsondata;
name;
constructor(private http: Http) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.http.get("http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users?id="+this.searchparam).
map(
(response) ⇒ response.json()
).
subscribe((data) ⇒ this.converttoarray(data))
}
converttoarray(data) {
console.log(data);
this.name = data[0].name;
}
}
对于get api ,我们将添加搜索参数id = this.searchparam。 searchparam等于2.我们需要json文件中id=2的详细信息。
app.component.html
{{name}}
这是浏览器的显示方式 -
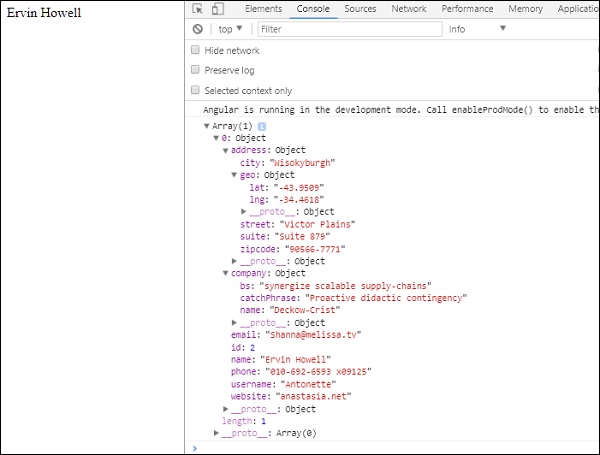
我们在浏览器中安装了数据,这是从http接收的。 浏览器控制台中显示相同的内容。 json中id=2名称显示在浏览器中。
Angular 4 - Forms
在本章中,我们将看到如何在Angular 4中使用表单。我们将讨论使用表单的两种方式 - 模板驱动表单和模型驱动表单。
模板驱动的表格
使用模板驱动的表单,大部分工作都在模板中完成; 并且使用模型驱动形式,大部分工作都在组件类中完成。
现在让我们考虑使用模板驱动表单。 我们将创建一个简单的登录表单并添加电子邮件ID,密码并在表单中提交按钮。 首先,我们需要从@angular/core导入到FormsModule,这在app.module.ts完成,如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule} from '@angular/router';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
import { SqrtPipe } from './app.sqrt';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
SqrtPipe,
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpModule,
FormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{path: 'new-cmp',component: NewCmpComponent}
])
],
providers: [MyserviceService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
所以在app.module.ts ,我们导入了FormsModule,并在imports数组中添加了相同的内容,如突出显示的代码所示。
现在让我们在app.component.html文件中创建表单。
<form #userlogin = "ngForm" (ngSubmit) = "onClickSubmit(userlogin.value)" >
<input type = "text" name = "emailid" placeholder = "emailid" ngModel>
<br/>
<input type = "password" name = "passwd" placeholder = "passwd" ngModel>
<br/>
<input type = "submit" value = "submit">
</form>
我们创建了一个带有输入标签的简单表单,其中包含电子邮件ID,密码和提交按钮。 我们已为其分配了类型,名称和占位符。
在模板驱动的表单中,我们需要通过添加ngModel指令和name属性来创建模型表单控件。 因此,无论我们希望Angular从表单访问我们的数据,都可以将ngModel添加到该标记,如上所示。 现在,如果我们必须阅读emailid和passwd,我们需要在其中添加ngModel。
如果你看到,我们还将ngForm添加到#userlogin 。 需要将ngForm指令添加到我们创建的表单模板中。 我们还添加了onClickSubmit函数并onClickSubmit分配了userlogin.value 。
现在让我们在app.component.ts创建函数并获取在表单中输入的值。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
componentproperty;
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
}
onClickSubmit(data) {
alert("Entered Email id : " + data.emailid);
}
}
在上面的app.component.ts文件中,我们定义了函数onClickSubmit。 当您单击表单提交按钮时,控件将进入上述功能。
这是浏览器的显示方式 -
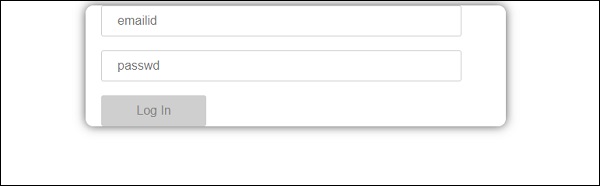
表单如下所示。 让我们在其中输入数据,并在提交功能中输入电子邮件ID。
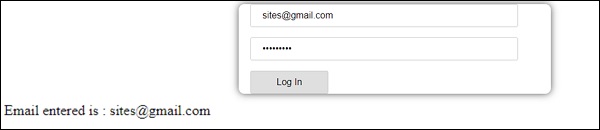
电子邮件ID显示在底部,如上面的屏幕截图所示。
模型驱动形式
在模型驱动形式中,我们需要从@ angular/forms导入ReactiveFormsModule并在imports数组中使用相同的。
app.module.ts.有一个更改app.module.ts.
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule} from '@angular/router';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
import { NewCmpComponent } from './new-cmp/new-cmp.component';
import { ChangeTextDirective } from './change-text.directive';
import { SqrtPipe } from './app.sqrt';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
SqrtPipe,
AppComponent,
NewCmpComponent,
ChangeTextDirective
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
HttpModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot([
{
path: 'new-cmp',
component: NewCmpComponent
}
])
],
providers: [MyserviceService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
在app.component.ts ,我们需要为模型驱动表单导入一些模块。 例如, import { FormGroup, FormControl } from '@angular/forms' 。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { MyserviceService } from './myservice.service';
import { FormGroup, FormControl } from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
componentproperty;
emailid;
formdata;
constructor(private myservice: MyserviceService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.todaydate = this.myservice.showTodayDate();
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
emailid: new FormControl("angular@gmail.com"),
passwd: new FormControl("abcd1234")
});
}
onClickSubmit(data) {this.emailid = data.emailid;}
}
变量formdata在类的开头初始化,并使用FormGroup初始化,如上所示。 变量emailid和passwd初始化为默认值,以显示在表单中。 如果您愿意,可以将其保留为空白。
这就是在表单UI中看到值的方式。
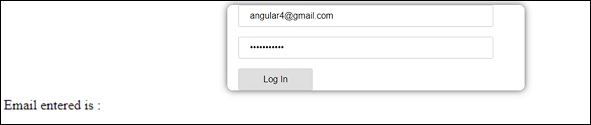
我们使用formdata来初始化表单值; 我们需要在UI app.component.html使用相同的表单。
<div>
<form [formGroup]="formdata" (ngSubmit) = "onClickSubmit(formdata.value)" >
<input type="text" class="fortextbox" name="emailid" placeholder="emailid"
formControlName="emailid">
<br/>
<input type="password" class="fortextbox" name="passwd"
placeholder="passwd" formControlName="passwd">
<br/>
<input type="submit" class="forsubmit" value="Log In">
</form>
</div>
<p>
Email entered is : {{emailid}}
</p>
在.html文件中,我们在方括号中使用formGroup作为表单; 例如,[formGroup] =“formdata”。 在提交时,该函数被调用onClickSubmit ,其formdata.value是formdata.value 。
使用输入标记formControlName 。 它被赋予了我们在app.component.ts文件中使用的值。
单击“提交”时,控件将传递给onClickSubmit函数,该函数在app.component.ts文件中定义。
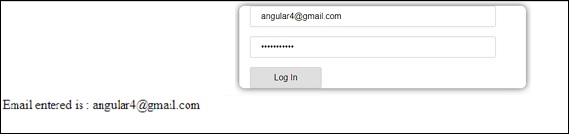
单击“登录”后,将显示该值,如上面的屏幕截图所示。
表格验证
现在让我们讨论使用模型驱动形式的表单验证。 您可以使用内置表单验证或使用自定义验证方法。 我们将使用表单中的两种方法。 我们将继续使用我们之前部分中创建的相同示例。 使用Angular 4,我们需要从@angular/forms导入Validators,如下所示 -
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms'
Angular具有内置验证器,如mandatory field, minlength, maxlength和pattern 。 这些将使用Validators模块进行访问。
您可以添加验证器或一系列验证器,以告知Angular特定字段是否必需。
现在让我们在其中一个输入文本框上尝试相同的操作,即电子邮件ID。 对于电子邮件ID,我们添加了以下验证参数 -
- Required
- 模式匹配
这是代码在app.component.ts进行验证的app.component.ts 。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
componentproperty;
emailid;
formdata;
ngOnInit() {
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
emailid: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.pattern("[^ @]*@[^ @]*")
])),
passwd: new FormControl("")
});
}
onClickSubmit(data) {this.emailid = data.emailid;}
}
在Validators.compose ,您可以在输入字段中添加要验证的内容列表。 现在,我们添加了required和pattern matching参数,只采用有效的电子邮件。
在app.component.html ,如果任何表单输入无效,则禁用提交按钮。 这样做如下 -
<div>
<form [formGroup] = "formdata" (ngSubmit) = "onClickSubmit(formdata.value)" >
<input type = "text" class = "fortextbox" name = "emailid" placeholder = "emailid"
formControlName = "emailid">
<br/>
<input type = "password" class = "fortextbox" name = "passwd"
placeholder = "passwd" formControlName = "passwd">
<br/>
<input type = "submit" [disabled] = "!formdata.valid" class = "forsubmit"
value = "Log In">
</form>
</div>
<p>
Email entered is : {{emailid}}
</p>
对于提交按钮,我们在方括号中添加了禁用,其值为 - !formdata.valid 。 因此,如果formdata.valid无效,则该按钮将保持禁用状态,用户将无法提交该按钮。
让我们看看它在浏览器中的工作原理 -
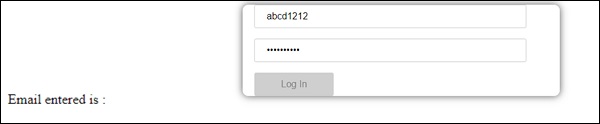
在上述情况下,输入的电子邮件ID无效,因此禁用登录按钮。 现在让我们尝试输入有效的电子邮件ID并查看差异。
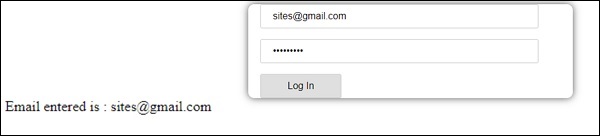
现在,输入的电子邮件ID有效。 因此,我们可以看到登录按钮已启用,用户将能够提交它。 这样,输入的电子邮件ID显示在底部。
现在让我们尝试使用相同的表单进行自定义验证。 对于自定义验证,我们可以定义自己的自定义函数并在其中添加所需的详细信息。 我们现在将看到一个相同的例子。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Angular 4 Project!';
todaydate;
componentproperty;
emailid;
formdata;
ngOnInit() {
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
emailid: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.pattern("[^ @]*@[^ @]*")
])),
passwd: new FormControl("", this.passwordvalidation)
});
}
passwordvalidation(formcontrol) {
if (formcontrol.value.length <'; 5) {
return {"passwd" : true};
}
}
onClickSubmit(data) {this.emailid = data.emailid;}
}
在上面的示例中,我们创建了一个函数password validation并在formcontrol的前一部分中使用了相同的函数--passwd passwd: new FormControl("", this.passwordvalidation) 。
在我们创建的函数中,我们将检查输入的字符长度是否合适。 如果字符小于5,则返回passwd为true,如上所示 - return {"passwd" : true}; 。 如果字符超过五个,则会将其视为有效并启用登录。
现在让我们看看它是如何在浏览器中显示的 -
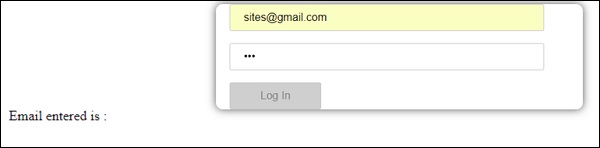
我们在密码中只输入了三个字符,并且禁用了登录。 要启用登录,我们需要超过五个字符。 现在让我们输入一个有效的字符长度并检查。
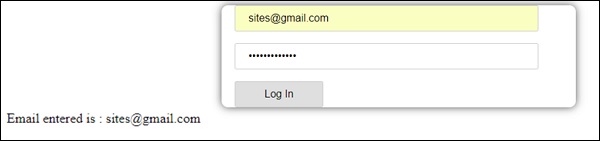
由于电子邮件ID和密码均有效,因此启用登录。 我们登录时,电子邮件显示在底部。
Angular 4 - Animations
动画在html元素之间添加了很多交互。 Angular2也提供动画。 与Angular 4的不同之处在于动画不再是@angular/core库的一部分,而是一个需要在app.module.ts导入的独立包。
首先,我们需要按如下方式导入库 -
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
需要将BrowserAnimationsModule添加到app.module.ts的导入数组中,如下所示 -
app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
在app.component.html ,我们添加了要动画的html元素。
<div>
<button (click)="animate()">Click Me</button>
<div [@myanimation] = "state" class="rotate">
<img src="assets/images/img.png" width="100" height="100">
</div>
</div>
对于主div,我们添加了一个按钮和一个带图像的div。 有一个click事件,调用animate函数。 对于div,添加@myanimation指令并将值赋予状态。
现在让我们看一下定义动画的app.component.ts 。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { trigger, state, style, transition, animate } from '@angular/animations';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'],
styles:[`
div{
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
width:200px;
}
.rotate{
width:100px;
height:100px;
border:solid 1px red;
}
`],
animations: [
trigger('myanimation',[
state('smaller',style({
transform : 'translateY(100px)'
})),
state('larger',style({
transform : 'translateY(0px)'
})),
transition('smaller <=> larger',animate('300ms ease-in'))
])
]
})
export class AppComponent {
state: string = "smaller";
animate() {
this.state= this.state == 'larger' ? 'smaller' : 'larger';
}
}
我们必须导入要在.ts文件中使用的动画功能,如上所示。
import { trigger, state, style, transition, animate } from '@angular/animations';
这里我们从@ angular/animations导入了触发器,状态,样式,过渡和动画。
现在,我们将动画属性添加到@Component()装饰器 -
animations: [
trigger('myanimation',[
state('smaller',style({
transform : 'translateY(100px)'
})),
state('larger',style({
transform : 'translateY(0px)'
})),
transition('smaller <=> larger',animate('300ms ease-in'))
])
]
触发器定义动画的开始。 它的第一个参数是要赋予动画需要应用的html标签的动画名称。 第二个参数是我们导入的函数 - 状态,转换等。
state函数涉及动画步骤,元素将在它们之间转换。 现在我们已经定义了两个状态,越来越小。 对于较小的状态,我们给出了样式transform:translateY(100px)和transform:translateY(100px) 。
Transition函数将动画添加到html元素。 第一个参数采用状态,即开始和结束; 第二个参数接受animate函数。 动画功能允许您定义过渡的长度,延迟和缓和。
现在让我们看一下.html文件,看看过渡函数是如何工作的
<div>
<button (click)="animate()">Click Me</button>
<div [@myanimation] = "state" class="rotate">
<img src="assets/images/img.png" width="100" height="100">
</div>
</div>
@component指令中添加了一个样式属性,它集中对齐div。 让我们考虑下面的例子来理解相同的 -
styles:[`
div{
margin: 0 auto;
text-align: center;
width:200px;
}
.rotate{
width:100px;
height:100px;
border:solid 1px red;
}
`],
这里,一个特殊的字符[``]用于向html元素添加样式(如果有的话)。 对于div,我们给出了app.component.ts文件中定义的动画名称。
在单击按钮时,它调用animate函数,该函数在app.component.ts文件中定义如下 -
export class AppComponent {
state: string = "smaller";
animate() {
this.state= this.state == ‘larger’? 'smaller' : 'larger';
}
}
定义状态变量,并将其默认值设置为较小。 animate函数会在单击时更改状态。 如果状态更大,它将转换为更小; 如果更小,它将转换为更大。
这是浏览器中的输出( http://localhost:4200/ )的样子 -
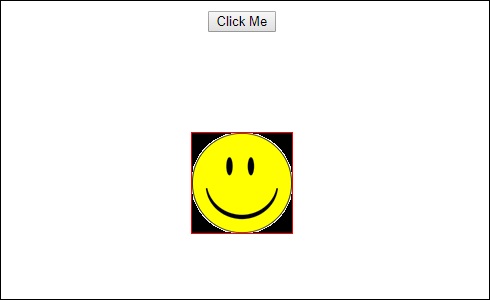
单击“ Click Me按钮后,图像的位置将更改,如以下屏幕截图所示 -
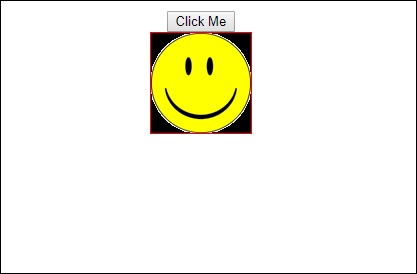
变换函数应用于y方向,单击Click Me按钮时,该方向从0变为100px。 图像存储在assets/images文件夹中。
Angular 4 - Materials
Materials为您的项目提供了许多内置模块。 自动完成,日期选择器,滑块,菜单,网格和工具栏等功能可用于Angular 4中的材质。
要使用材料,我们需要导入包。 Angular 2还具有上述所有功能,但它们可作为@ angular/core模块的一部分使用。 Angular 4提出了一个单独的模块@angular/materials. 。 这有助于用户导入所需的材料。
要开始使用材料,您需要安装两个包 - 材料和cdk。 材质组件依赖于动画模块来获得高级功能,因此您需要相同的动画包,即@ angular/animations。 该包已在上一章中进行了更新。
npm install --save @angular/material @angular/cdk
现在让我们看看package.json。 @angular/material和@angular/cdk已安装。
{
"name": "angularstart",
"version": "0.0.0",
"license": "MIT",
"scripts": {
"ng": "ng",
"start": "ng serve",
"build": "ng build",
"test": "ng test",
"lint": "ng lint",
"e2e": "ng e2e"
},
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"@angular/animations": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/cdk": "^2.0.0-beta.8",
"@angular/common": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/compiler": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/core": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/forms": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/http": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/material": "^2.0.0-beta.8",
"@angular/platform-browser": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/platform-browser-dynamic": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/router": "^4.0.0",
"core-js": "^2.4.1",
"rxjs": "^5.1.0",
"zone.js": "^0.8.4"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@angular/cli": "1.2.0",
"@angular/compiler-cli": "^4.0.0",
"@angular/language-service": "^4.0.0",
"@types/jasmine": "~2.5.53",
"@types/jasminewd2": "~2.0.2",
"@types/node": "~6.0.60",
"codelyzer": "~3.0.1",
"jasmine-core": "~2.6.2",
"jasmine-spec-reporter": "~4.1.0",
"karma": "~1.7.0",
"karma-chrome-launcher": "~2.1.1",
"karma-cli": "~1.0.1",
"karma-coverage-istanbul-reporter": "^1.2.1",
"karma-jasmine": "~1.1.0",
"karma-jasmine-html-reporter": "^0.2.2",
"protractor": "~5.1.2",
"ts-node": "~3.0.4",
"tslint": "~5.3.2",
"typescript": "~2.3.3"
}
}
我们已经突出显示了为处理材料而安装的软件包。
我们现在将在父模块中导入模块 - app.module.ts ,如下所示。
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { MdButtonModule, MdMenuModule, MdSidenavModule } from '@angular/material';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
MdButtonModule,
MdMenuModule,
FormsModule,
MdSidenavModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
在上面的文件中,我们从@ angular/materials导入了以下模块。
import { MdButtonModule, MdMenuModule, MdSidenavModule } from '@angular/material';
并且在进口数组中使用相同的内容,如下所示 -
imports: [
BrowserModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
MdButtonModule,
MdMenuModule,
FormsModule,
MdSidenavModule
]
app.component.ts如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
myData: Array<any>;
constructor() {}
}
现在让我们在app.component.html添加材料。
<button md-button [mdMenuTriggerFor]="menu">Menu</button>
<md-menu #menu="mdMenu">
<button md-menu-item>
File
</button>
<button md-menu-item>
Save As
</button>
</md-menu>
<md-sidenav-container class="example-container">
<md-sidenav #sidenav class="example-sidenav">
Angular 4
</md-sidenav>
<div class="example-sidenav-content">
<button type="button" md-button (click)="sidenav.open()">
Open sidenav
</button>
</div>
</md-sidenav-container>
在上面的文件中,我们添加了Menu和SideNav。
Menu
要添加菜单,使用《md-menu》《/md-menu》 。 file和Save As项目将添加到md-menu下的按钮中。 有一个主按钮添加了Menu 。 通过使用[mdMenuTriggerFor]=”menu”并# in 《md-menu》使用带有# in 《md-menu》的菜单,给出# in 《md-menu》 。
SideNav
要添加sidenav,我们需要《md-sidenav-container》《/md-sidenav-container》 。 《md-sidenav》《/md-sidenav》作为子容器添加到容器中。 还添加了另一个div,它通过使用(click)=”sidenav.open()”来触发sidenav。 以下是浏览器中菜单和sidenav的显示 -

单击opensidenav ,它会显示侧栏,如下所示 -

单击“菜单”后,您将获得两个项目“ File和“ Save As ,如下所示 -

现在让我们使用材料添加一个日期选择器。 要添加日期选择器,我们需要导入显示datepicker所需的模块。
在app.module.ts ,我们为app.module.ts导入了以下模块,如下所示。
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import { MdDatepickerModule, MdInputModule, MdNativeDateModule } from '@angular/material';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
BrowserAnimationsModule,
FormsModule,
MdDatepickerModule,
MdInputModule,
MdNativeDateModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
在这里,我们导入了MdDatepickerModule, MdInputModule,和MdNativeDateModule等模块。
现在, app.component.ts如下所示 -
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {
myData: Array<any>;
constructor() {}
}
app.component.html如下所示 -
<md-input-container>
<input mdInput [mdDatepicker]="picker" placeholder="Choose a date">
<button mdSuffix [mdDatepickerToggle]="picker"></button>
</md-input-container>
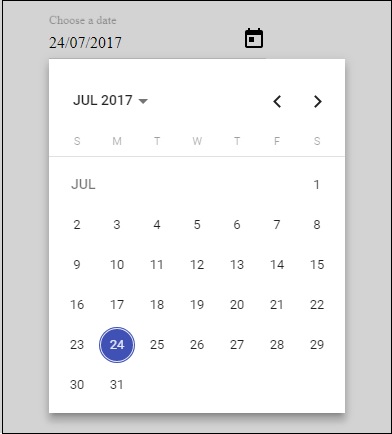
<md-datepicker #picker></md-datepicker>
这就是datepicker在浏览器中的显示方式 -
Angular 4 - CLI
Angular CLI使您可以轻松地开始使用任何Angular项目。 Angular CLI附带的命令可以帮助我们快速创建和启动项目。 现在让我们来看看可用于创建项目,组件和服务,更改端口等的命令。
要使用Angular CLI,我们需要在我们的系统上安装它。 让我们使用以下命令 -
npm install -g @angular/cli
要创建新项目,我们可以在命令行中运行以下命令,然后将创建项目。
ng new PROJECT-NAME
cd PROJECT-NAME
ng serve //
ng serve //将编译,您可以在浏览器中看到项目的输出 -
http://localhost:4200/
4200是创建新项目时使用的默认端口。 您可以使用以下命令更改端口 -
ng serve --host 0.0.0.0 --port 4201
下表列出了使用Angular 4项目时所需的一些重要命令。
| Component | ng g组件新组件 |
| Directive | ng g指令new-directive |
| Pipe | ng g pipe new-pipe |
| Service | ng g service new-service |
| Module | ng g module my-module |
无论何时创建新模块,组件或服务,都会在父模块app.module.ts更新相同的引用。
Angular 4 - Examples
在本章中,我们将讨论与Angular 4相关的一些示例。
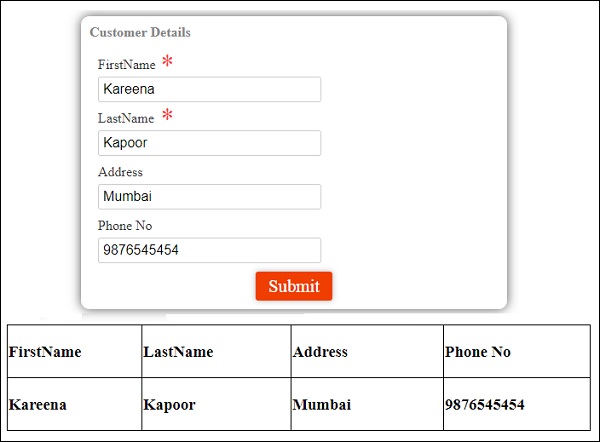
首先,我们创建了一个示例,其中显示了一个输入为username和password的登录表单。 输入正确的值后,它将进入内部并显示另一个表格,您可以输入客户详细信息。 此外,我们还创建了四个组件 - 页眉,页脚,用户登录和主页。
使用以下命令创建组件 -
ng g组件标题
C:\ngexamples\aexamples>ng g component header
installing component
create src\app\header\header.component.css
create src\app\header\header.component.html
create src\app\header\header.component.spec.ts
create src\app\header\header.component.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
ng g组件页脚
C:\ngexamples\aexamples>ng g component footer
installing component
create src\app\footer\footer.component.css
create src\app\footer\footer.component.html
create src\app\footer\footer.component.spec.ts
create src\app\footer\footer.component.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
ng g组件用户登录
C:\ngexamples\aexamples>ng g component userlogin
installing component
create src\app\userlogin\userlogin.component.css
create src\app\userlogin\userlogin.component.html
create src\app\userlogin\userlogin.component.spec.ts
create src\app\userlogin\userlogin.component.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
ng g组件主页
C:\ngexamples\aexamples>ng g component mainpage
installing component
create src\app\mainpage\mainpage.component.css
create src\app\mainpage\mainpage.component.html
create src\app\mainpage\mainpage.component.spec.ts
create src\app\mainpage\mainpage.component.ts
update src\app\app.module.ts
在app.module.ts ,父模块在创建时添加了所有组件。 该文件如下 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { RouterModule, Routes} froms '@angular/router';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import {MdTableModule} from '@angular/material';
import {HttpModule} from "@angular/http";
import {MdInputModule} from '@angular/material';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HeaderComponent } from './header/header.component';
import { FooterComponent } from './footer/footer.component';
import { UserloginComponent } from './userlogin/userlogin.component';
import { MainpageComponent } from './mainpage/mainpage.component';
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: UserloginComponent
},
{
path: 'app-mainpage',
component: MainpageComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeaderComponent,
FooterComponent,
UserloginComponent,
MainpageComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes),
BrowserAnimationsModule,
HttpModule,
MdTableModule,
MdInputModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
上面创建的组件已添加 -
import { HeaderComponent } from './header/header.component';
import { FooterComponent } from './footer/footer.component';
import { UserloginComponent } from './userlogin/userlogin.component';
import { MainpageComponent } from './mainpage/mainpage.component';
组件也在声明中添加 -
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeaderComponent,
FooterComponent,
UserloginComponent,
MainpageComponent
],
在父app.component.html ,我们添加了用户将看到的文件的主要结构。
<div class="mainpage">
<app-header></app-header>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
<app-footer></app-footer>
</div>
我们创建了一个div并添加了《app-header》《/app-header》 , 《router-outlet》《/router-outlet》和《app-footer》《/app-footer》 。
《router-outlet》《/router-outlet》用于在一个页面到另一个页面之间导航。 这里,页面是登录表单,一旦成功,它将重定向到主页,即客户表单。
要首先获取登录表单,然后获取mainpage.component.html,更改将在app.module.ts中完成,如下所示 -
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { RouterModule, Routes} from '@angular/router';
import { BrowserAnimationsModule } from '@angular/platform-browser/animations';
import {MdTableModule} from '@angular/material';
import {HttpModule} from "@angular/http";
import {MdInputModule} from '@angular/material';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { HeaderComponent } from './header/header.component';
import { FooterComponent } from './footer/footer.component';
import { UserloginComponent } from './userlogin/userlogin.component';
import { MainpageComponent } from './mainpage/mainpage.component';
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: UserloginComponent
},
{
path: 'app-mainpage',
component: MainpageComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
HeaderComponent,
FooterComponent,
UserloginComponent,
MainpageComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
ReactiveFormsModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(appRoutes),
BrowserAnimationsModule,
HttpModule,
MdTableModule,
MdInputModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
我们从@anuglar/router导入了RouterModule和Routes 。 在导入中,RouterModules将appRoutes作为上面定义的param -
const appRoutes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: UserloginComponent
},
{
path: 'app-mainpage',
component: MainpageComponent
}
];
路由采用组件数组,默认情况下调用userloginComponent。
在userlogin.component.ts ,我们已导入路由器并根据条件导航到mainpage.component.html,如下所示 -
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
import { Router} from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-userlogin',
templateUrl: './userlogin.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./userlogin.component.css']
})
export class UserloginComponent implements OnInit {
formdata;
constructor(private router: Router) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
uname: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.minLength(6)
])),
passwd: new FormControl("", this.passwordvalidation)
});
}
passwordvalidation(formcontrol) {
if (formcontrol.value.length < 5) {
return {"passwd" : true};
}
}
onClickSubmit(data) {
console.log(data.uname);
if (data.uname=="systemadmin" && data.passwd=="admin123") {
alert("Login Successful");
this.router.navigate(['app-mainpage'])
} else {
alert("Invalid Login");
return false;
}
}
}
以下是app.component.ts的.ts文件。 其中仅包含默认详细信息。
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css']
})
export class AppComponent {title = 'app';}
现在让我们显示每个组件文件的详细信息。 首先,我们将首先采用标头组件。 对于新组件,将创建四个文件header.component.ts, header.component.html, header.component.css, and header.component.spec.ts 。
header.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-header',
templateUrl: './header.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./header.component.css']
})
export class HeaderComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() {}
}
header.component.html
<div>
<hr />
</div>
我们还没有添加任何CSS。 这使得header.component.css文件为空。 此外, header.compoent.spec.ts文件为空,因为此处不考虑测试用例。
对于标题,我们将绘制一条水平线。 可以添加徽标或任何其他细节,使标题看起来更具创意。
现在让我们考虑创建一个页脚组件。
对于页脚组件,将创建footer.component.ts, footer.component.html, footer.component.spec.ts and footer.component.css文件。
footer.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-footer',
templateUrl: './footer.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./footer.component.css']
})
export class FooterComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit() { }
}
footer.component.html
<hr/>
由于我们没有添加任何css,因此footer.component.css文件为空。 此外, footer.compoent.spec.ts文件为空,因为此处不考虑测试用例。
对于页脚,我们将绘制一条水平线,如.html文件中所示。
现在让我们看看userlogin组件的工作原理。 创建的userlogin组件的以下文件是userlogin.component.css, userlogin.component.html, userlogin.component.ts,和userlogin.component.spec.ts.
文件的详细信息如下 -
userlogin.component.html
<div class="form_container">
<form [formGroup]="formdata" (ngSubmit) = "onClickSubmit(formdata.value)" >
<header>Login</header>
<label>Username <span>*</span></label>
<input type="text" name="uname" formControlName="uname"/>
<div class="help">At least 6 character</div>
<label>Password <span>*</span></label>
<input type="password" class="fortextbox" name="passwd" formControlName="passwd"/>
<div class="help">Use upper and lowercase lettes as well</div>
<button [disabled]="!formdata.valid" value="Login">Login</button>
</form>
</div>
在这里,我们创建了带有两个输入控件Username和Password表单。 这是一种模型驱动形式的方法,其细节在第14章 - 表格中进行了解释。
我们认为用户名和密码是强制性的,因此在ts中添加了相同的验证。 单击提交按钮后,控件将传递给onClickSubmit ,该onClickSubmit在ts文件中定义。
userlogin.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
import { Router} from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-userlogin',
templateUrl: './userlogin.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./userlogin.component.css']
})
export class UserloginComponent implements OnInit {
formdata;
constructor(private router: Router) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
uname: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.minLength(6)
])),
passwd: new FormControl("", this.passwordvalidation)
});
}
passwordvalidation(formcontrol) {
if (formcontrol.value.length < 5) {
return {"passwd" : true};
}
}
onClickSubmit(data) {
console.log(data.uname);
if (data.uname == "systemadmin" && data.passwd == "admin123") {
alert("Login Successful");
this.router.navigate(['app-mainpage'])
}
}
}
对于formcontrol和验证,将导入模块,如下所示
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
当用户和密码正确时,我们需要路由器导航到不同的组件。 为此,导入路由器如下所示 -
import { Router} from '@angular/router';
在ngOnInit ,完成表单的验证。 我们需要用户名超过六个字符,该字段是必填字段。 同样的条件也适用于密码。
点击提交后,我们可以检查用户名是否为systemadmin ,密码是admin123 。 如果是,则会出现一个对话框,显示Login Successful ,并且路由器导航到app-mainpage,它是主页组件的选择器。
在userlogin.component.css文件中为表单添加了css -
.form_container{
margin : 0 auto;
width:600px;
}
form {
background: white;
width: 500px;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
font-family: lato;
position: relative;
color: #333;
border-radius: 10px;
}
form header {
background: #FF3838;
padding: 30px 20px;
color: white;
font-size: 1.2em;
font-weight: 600;
border-radius: 10px 10px 0 0;
}
form label {
margin-left: 20px;
display: inline-block;
margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 5px;
position: relative;
}
form label span {
color: #FF3838;
font-size: 2em;
position: absolute;
left: 2.3em;
top: -10px;
}
form input {
display: block;
width: 50%;
margin-left: 20px;
padding: 5px 20px;
font-size: 1em;
border-radius: 3px;
outline: none;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
}
form .help {
margin-left: 20px;
font-size: 0.8em;
color: #777;
}
form button {
position: relative;
margin-top: 30px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, 0);
font-family: inherit;
color: white;
background: #FF3838;
outline: none;
border: none;
padding: 5px 15px;
font-size: 1.3em;
font-weight: 400;
border-radius: 3px;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 10px rgba(51, 51, 51, 0.4);
cursor: pointer;
transition: all 0.15s ease-in-out;
}
form button:hover {
background: #ff5252;
}
userlogin.component.spec.ts文件为空,因为现在没有测试用例。
现在让我们讨论主页组件的工作原理。 为主页组件创建的文件是mainpage.component.ts, mainpage.component.html, mainpage.component.css,和mainpage.component.spect.ts 。
mainpage.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit, ViewChild} from '@angular/core';
import { FormGroup, FormControl, Validators} from '@angular/forms';
import {Http, Response, Headers, RequestOptions } from "@angular/http";
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
@Component({
selector: 'app-mainpage',
templateUrl: './mainpage.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./mainpage.component.css']
})
export class MainpageComponent implements OnInit {
formdata;
cutomerdata;
constructor(private http: Http) { }
stateCtrl: FormControl;
ngOnInit() {
this.formdata = new FormGroup({
fname: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.minLength(3)
])),
lname: new FormControl("", Validators.compose([
Validators.required,
Validators.minLength(3)
])),
address:new FormControl(""),
phoneno:new FormControl("")
});
}
onClickSubmit(data) {
document.getElementById("custtable").style.display="";
this.cutomerdata = [];
for (var prop in data) {
this.cutomerdata.push(data[prop]);
}
console.log(this.cutomerdata);
}
}
我们创建了一个客户表单,其中包含姓名,姓氏,地址和电话号码。 使用ngOnInit函数完成相同的验证。 单击提交后,控件将进入onClickSubmit函数。 这里,用于显示输入细节的表格可见。
customerdata从json转换为数组,以便我们可以在表格中使用相同的ngFor,这在.html文件中完成,如下所示。
mainpage.component.html
<div class="form_container">
<form [formGroup]="formdata" (ngSubmit) = "onClickSubmit(formdata.value)" >
<header>Customer Details</header>
<label>FirstName <span>*</span></label>
<input type="text" name="fname" formControlName="fname"/>
<label>LastName <span>*</span></label>
<input type="text" name="lname" formControlName="lname"/>
<label>Address <span></span></label>
<input type="text" name="address" formControlName="address"/>
<label>Phone No <span></span></label>
<input type="text" name="phoneno" formControlName="phoneno"/>
<button [disabled]="!formdata.valid" value="Submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<br/>
<div id="custtable" style="display:none;margin:0 auto;">
<table>
<tr>
<td>FirstName</td>
<td>LastName</td>
<td>Address</td>
<td>Phone No</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td *ngFor="let data of cutomerdata">
<h5>{{data}}</h5>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
这里,第一个div有客户详细信息,第二个div有表,这将显示输入的详细信息。 userlogin和客户详细信息的显示如下所示。 这是包含登录表单和页眉和页脚的页面。
输入详细信息后,显示如下所示
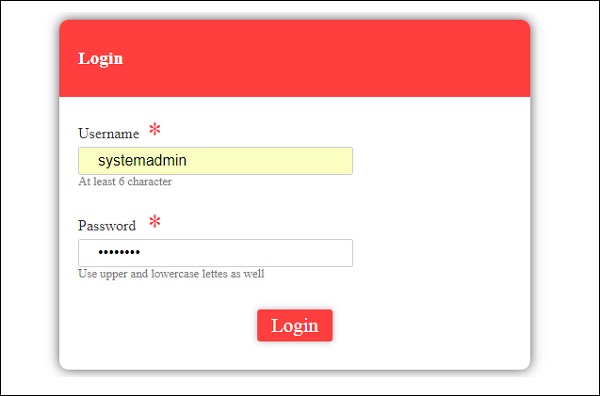
单击“提交”后,将出现一个对话框,显示“登录成功”。
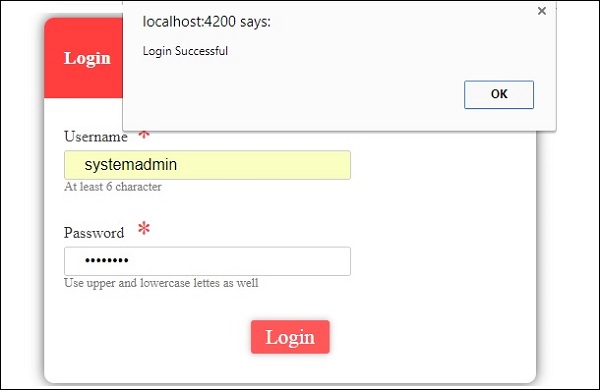
如果细节无效,则会出现一个对话框,显示无效登录,如下所示 -
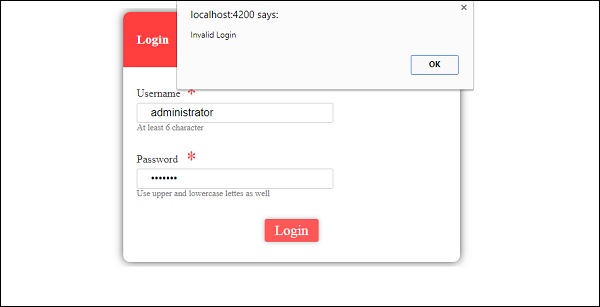
如果登录成功,它将进入下一个形式的客户详细信息,如下所示 -
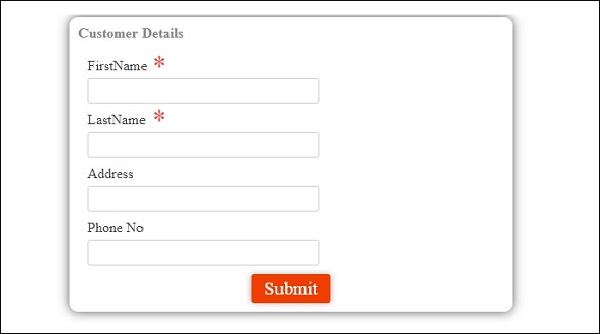
输入并提交详细信息后,将出现一个对话框,显示添加的客户详细信息,如下面的屏幕截图所示 -
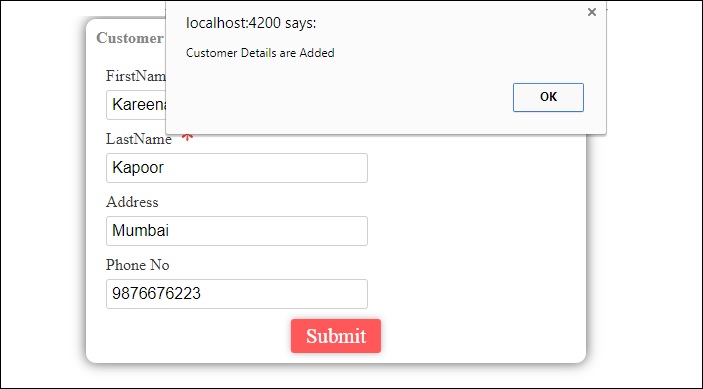
当我们在上面的屏幕截图中单击“确定”时,将显示详细信息,如下面的屏幕截图所示 -