DSA - 选择排序(Selection Sort)
选择排序是一种简单的排序算法。 这种排序算法是一种就地比较算法,其中列表分为两部分,左端的排序部分和右端的未排序部分。 最初,排序部分为空,未排序部分为整个列表。
最小元素从未排序数组中选择,并与最左边的元素交换,该元素成为排序数组的一部分。 此过程继续将未排序的数组边界向右移动一个元素。
该算法不适用于大数据集,因为其平均和最差情况复杂度为0(n 2 ),其中n是项目数。
选择排序如何工作?
以下面描述的数组为例。
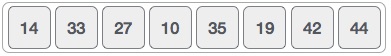
对于排序列表中的第一个位置,将按顺序扫描整个列表。 当前存储14的第一个位置,我们搜索整个列表并发现10是最低值。
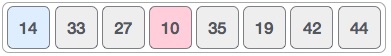
所以我们用10代替14.在一次迭代10之后,恰好是列表中的最小值,出现在排序列表的第一个位置。

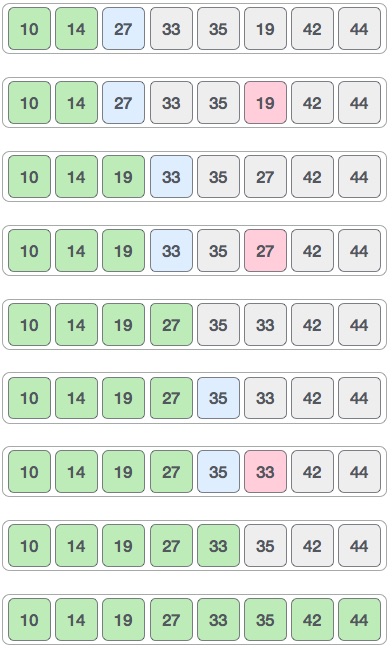
对于存在33的第二个位置,我们开始以线性方式扫描列表的其余部分。

我们发现14是列表中的第二低值,它应该出现在第二位。 我们交换这些值。

在两次迭代之后,两个最小值以排序的方式位于开头。

相同的过程应用于数组中的其余项。
以下是整个分拣过程的图示 -
现在,让我们学习一些选择排序的编程方面。
算法 (Algorithm)
<b class="notranslate">Step 1</b> − Set MIN to location 0
<b class="notranslate">Step 2</b> − Search the minimum element in the list
<b class="notranslate">Step 3</b> − Swap with value at location MIN
<b class="notranslate">Step 4</b> − Increment MIN to point to next element
<b class="notranslate">Step 5</b> − Repeat until list is sorted
伪代码 (Pseudocode)
procedure selection sort
list : array of items
n : size of list
for i = 1 to n - 1
/* set current element as minimum*/
min = i
/* check the element to be minimum */
for j = i+1 to n
if list[j] < list[min] then
min = j;
end if
end for
/* swap the minimum element with the current element*/
if indexMin != i then
swap list[min] and list[i]
end if
end for
end procedure
要了解C编程语言中的选择排序实现,请单击此处 。
